Do Amphibians Lay Eggs

Have you ever thought about whether amphibians lay eggs? Or where do amphibians lay eggs?
Amphibians lay soft-jelly-like eggs without shells in water, and their fertilization is external. They usually lay eggs in clusters. Without water, their eggs do not survive and dry out. They have to go through many stages to become adults.
The method of laying eggs and their life cycle is special. In this blog, we explain everything in detail, from egg laying to development, with examples that clear your concepts.
What are Amphibians
Amphibians are unique animals that belong to the class Amphibia. These are the animals that live both on land and in water during their lives. The word Amphibians comes from the Greek words Amphi, meaning both, and bios, meaning life, due to their dual lifestyle. Frogs, toads, newts, and salamanders are included in this group.
- One of the most interesting characteristics is that they reproduce by laying eggs, unlike mammals, which give birth to live young. These eggs are specially adapted to their environment and play a key role in the amphibian life cycle.
- Amphibians generally lay their eggs in ponds, lakes, rivers, or wet soil. Some species even attach their eggs to leaves or underwater plants to provide protection and support.
Do Amphibians Lay Eggs?
Yes, all amphibians lay eggs, and this is one of the defining features of the group.
- However, unlike reptiles or birds, they lack a hard shell.
- This makes them highly dependent on water and moist environments because they can easily dry out if exposed to the air.
- Most amphibians lay their eggs in freshwater such as Ponds, lakes, rivers wet soil.
- Some species attach their eggs to plants, leaves, or rocks in water. Some lay eggs in foam nests or hidden, moist places on land
For Example:
- Frogs usually lay eggs in water.
- Toads lay eggs in long strings in ponds.
- Salamanders may lay eggs under stones or leaves in water.
- Some caecilians lay eggs in moist soil.
Do Amphibians and Reptiles Lay Amniotic Eggs?
Aminotic eggs have a hard or leathery shell and special membranes that protect the embryo and allow it to survive on land without drying out.
- Reptiles lay amniotic eggs with hard or leathery shells. Their eggs can survive on land without water. Their fertilization is internal. For example, snakes, lizards, turtles, crocodiles.
- Amphibians do not lay amniotic eggs. They lay soft,jelly-like eggs. Their eggs cannot survive out of water because they dry easily. Fertilization is external. For example, Frogs, toads, and salamanders.
Characteristics of Amphibian Eggs
There are some characteristics of Amphibian eggs. Their eggs are soft, jelly-like, need moist places, and you can see the developing embryo inside the egg. Here is a brief description;
- Soft and jelly-like:
Unlike bird eggs or reptile eggs, amphibian eggs are soft and jelly-like eggs with no hard shell, and cannot survive without water.
- Moisture dependent:
They must stay in water or a damp place to survive. Otherwise, they will dry out if placed in the air for a long time.
- Transparent or semi-transparent:
The eggs are often clear, allowing you to see the developing embryo inside.
- Size
Amphibians are usually small, but some species, like salamanders, lay larger eggs.
- Egg clusters:
Frogs and toads often lay hundreds of eggs together in a jelly-like mass, while some salamanders lay eggs individually.
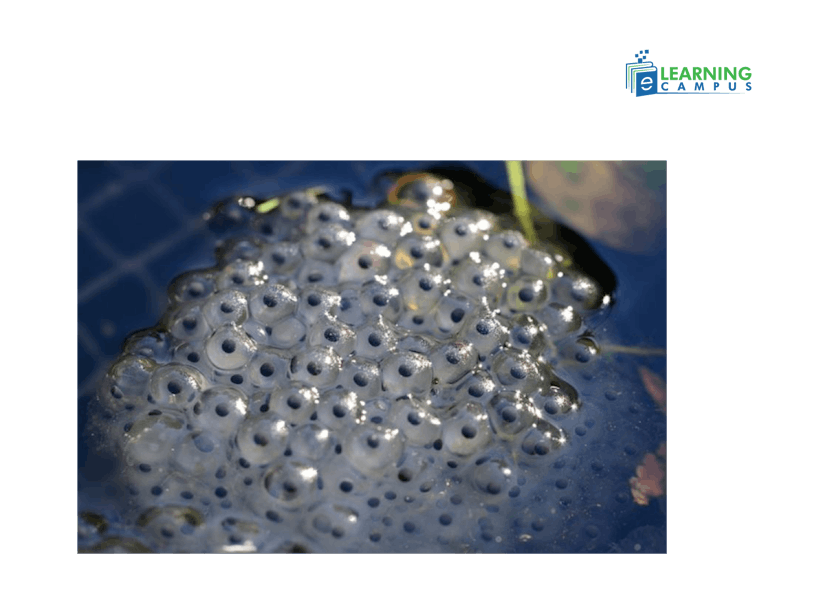
Amphibian Life-Cycle
After laying eggs, most amphibians go through a metamorphic life cycle. Reptiles lack this feature, which is a major biological difference between them. They have no metamorphosis. Their offspring hatch from eggs that are identical to their parents. But amphibians have to pass several stages to become adults. Such as the egg stage, larval stage, metamorphosis, and then the adult stage. Here are examples of a frog.
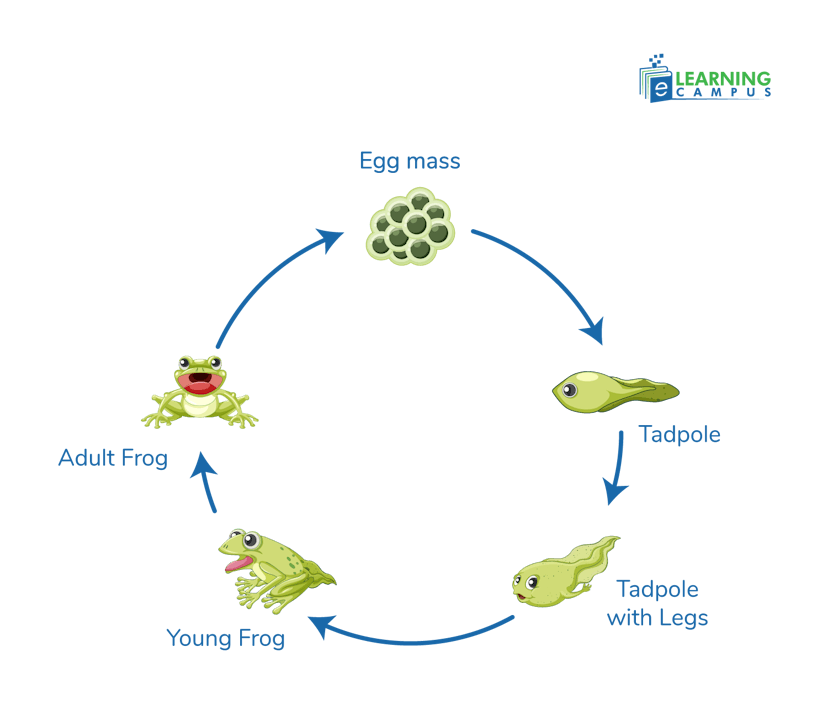
1. Egg stage: Eggs are laid in water or moist places to prevent drying out. Eggs are usually laid in large clusters called spawn. Frog eggs are called frogspawn.
2. Larval Stage: Eggs hatch into larvae, such as a tadpole in frogs. At this stage, they usually have gills and live entirely in water.
3. Metamorphosis: Larvae gradually develop lungs, legs, and other adult features, transforming into adults.
4. Young Frog: This is the stage between a tadpole and an adult Frog. It has legs, but may have a small tail. Breathe using lungs and start to live on both land and in water.
5. Adult Stage: The tail completely disappears. Adult amphibians live on land and water and are ready to reproduce.
Want to learn more. Get help with our Expert Online Tutors.
Fertilization in Amphibians?
Most amphibians show external fertilization. It means females lay eggs in water. It means;
- Fertilization happens outside the body, usually in water.
- The male releases sperm over the eggs.
- The sperm meet the eggs in water. This joining forms a fertilized egg.
Why is Water Important for Amphibians to Lay Eggs
Water is necessary for amphibians to lay eggs. Because they do not have hard shells for protection, that’s why they lay eggs in water that keeps them moist and helps them in development. Here are the points;
- Amphibian eggs do not have hard shells.
- Water keeps the eggs moist and safe.
- Fertilization cannot happen properly without water.
Conclusions
Every species has unique traits or behaviors that help in its environment, and these traits make it different from others. Amphibians and reptiles both reproduce by laying eggs, but their eggs are different. Amphibians lay soft-jelly like eggs that need water to survive, while reptiles lay amniotic eggs with hard or leathery eggs that can survive on land. Such differences not only ensure survival but also make each species distinct from one another.
Learn science online with Expert Tutors
Want to learn more about nature or science topics? Our expert online science tutors can help you. They will help with your homework, preparation for exams, and cover key topics. Get benefits with our online tutoring service and boost your grades in Science now!

Related Amphibians Articles
Curated science articles exploring amphibian species, biology, and habitats.






