Reptiles and Amphibians

Have you ever thought about whether a frog, turtle, or lizard is a reptile or an amphibian? These are a group of vertebrates that have lived on Earth for millions of years. Although both reptiles and amphibians are cold-blooded, their lifestyles and body structures are different. Their similarities, differences, and importance help us to understand the surprising facts about their existence on Earth.
In this blog, we will explore the characteristics, examples, lifestyles, and ecological roles of reptiles and amphibians, along with key differences that make each group truly interesting.
What are Reptiles or Amphibians?
Reptiles and Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates, which means that they cannot control their body temperature internally. They need sunlight to maintain their body temperature. However, they belong to different classes and have unique lifecycles.
Reptiles
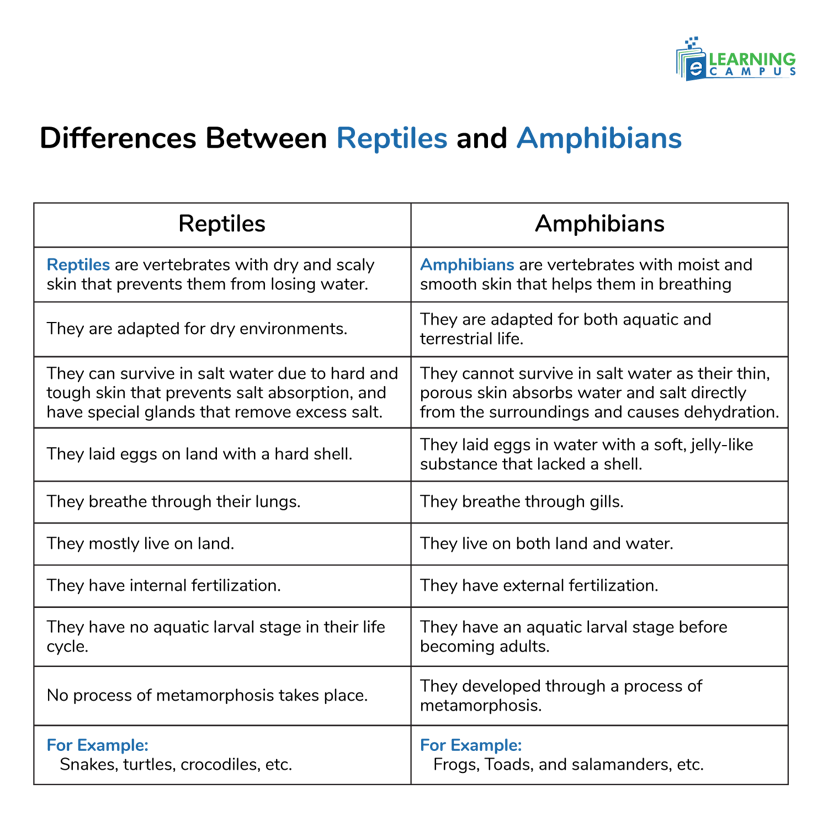
Reptiles belong to the class Reptilia. These are cold-blooded vertebrates with dry, scaly skin that prevents water loss. The hard, scaly skin helps them to survive in hot and dry climates. Their hard skin protects them from toxins and pollutants, preventing harmful substances from entering their bodies.
They breathe through lungs and lay eggs with hard or leathery shells on land.
Reptiles have internal fertilization, which means that eggs are fertilized inside the female's body, allowing them to reproduce on land.

Characteristics of Reptiles
Here are the main characteristics of reptiles.
- Cold-blooded (Ectothermic)
They are cold-blooded means their body temperature changes with the environment. They depend on shade or sun to stay warm or cool.
- Body structure
Most reptiles have four short legs and clawed toes for crawling. However, snakes do not have legs but still move effectively by slithering.
- Scaly, Dry skin
Their skin is dry and hard, which prevents them from losing water and protects them from any attack or injury.
- Eggs with leathery shells
Most reptiles lay eggs on land. Their eggs have tough, leathery shells that protect the baby inside from drying out.
- Breathe with lungs
Reptiles breathe only through lungs throughout their lives, even if they live in water.
- Heart
Reptiles have three chambers with two atria and one ventricle. But crocodiles have four chambers similar to mammals.
- Internal fertilization
Reproduction happens inside the female’s body, ensuring eggs are fertilized before being laid. Young ones hatch fully developed offspring, and there is no larval stage, or they do not go through metamorphosis.
- Slow metabolism
Due to their cold-blooded nature, their metabolism is slow. This allows them to survive long periods without food.
- Diet
Many reptiles are carnivores feeding on insects, small animals, and fish. Some reptiles, such as turtles, are omnivores and also eat plants.
Amphibians
Amphibians belong to the class Amphibia. They can begin their life in water and then on land. They have porous and thin skin that easily absorbs pollutants, making them more sensitive to water quality. Because of this difference, amphibians cannot survive in salt water, but reptiles can live in salt water. They lay their eggs on water without shells. They start their life as larvae with gills and transform into adults with lungs through metamorphosis.
Amphibians have external fertilization, which means fertilization takes place outside the body, and they lay eggs in water.

Characteristics of Amphibians
Here are the main characteristics of amphibians:
- Cold-blooded
Amphibians are also cold-blooded. They cannot regulate their body temperature, and they also need sun or shade to stay warm or cool.
- Live on land and in Water
Amphibians spend the initial part of their life in water and then live on land as adults. For example, frog start their life in water as a larva, then later move to land.
- Limbs
Amphibians usually have four limbs; front limbs are short, hind limbs are long and muscular for jumping.
- Heart
Amphibians have a three-chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle
- Lifecycle and metamorphosis
They go through proper life cycle states in their life, for example, from egg to tadpole(larva), then to adult. This change is called metamorphosis. Tadpoles breathe through gills, but when they become adult then they breathe through skin and lungs.
- Smooth and Thin skin
Amphibians have Soft, moist, and smooth skin without scales, which helps them in breathing and absorb water, but also means they must live in moist environments to prevent drying out.
- Breathe through the Lungs
Amphibians use gills when young and later develop lungs. As an adult, they can also breathe through their skin.
- Lay eggs in water
Their eggs are soft and jelly-like without a shell. So they must be laid on water to prevent drying out.
- Diet
Most adult amphibians are carnivores, eating insects, worms, and small animals.
Are snakes Reptiles or Amphibians?
A snake is a reptile, not an amphibian. Because they have scales and hard skin on their body, breathe through lungs, lay hard-shelled eggs on land, and live on land, not in water like amphibians.
Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians
Both reptiles and amphibians belong to an ancient line of cold-blooded vertebrates, lay eggs, and depend on their surroundings for warmth and survival; then what's the difference? Many people confuse these two, but here are the key points between reptiles and amphibians that make them different from each other. Here are the differences:
Is Turtle a Reptile or an Amphibian
A turtle is a reptile, not an amphibian, due to the following reasons:
- The turtle has scales on their skin and shell, but amphibians have smooth and moist skin.
- Turtles breathe through lungs, but amphibians breathe through gills.
- Turtles lay hard-shelled eggs on land, while amphibians lay soft and jelly-like eggs in water.
- Like other reptiles, turtles' body temperature changes with the environment.
Is a Frog a Reptile or an Amphibian?
A Frog is an amphibian due to the following reasons ;
- They live both on land and in water. Frogs start their life in water as tadpoles and later live on land and in water as adults.
- Frogs have moist and soft skin that helps them breathe.
- Frogs lay soft, jelly-like eggs in water, not hard-shelled like reptiles.
- Young frogs have gills to breathe underwater. Adult frogs develop lungs and can also absorb oxygen through their skin.
Is a Lizard a Reptile or an Amphibian?
Lizards are reptiles, not amphibians, due to the following reason:
- Lizards have dry and scaly skin, but amphibians have smooth and moist skin.
- Lizards breathe through lungs, not through gills.
- Lizards lay eggs with hard shells on land.
- Like other reptiles, lizards are cold-blooded and need sunlight to stay warm.
Conclusions
Reptiles and amphibians are both amazing groups of cooled animals that with their own traits and roles in nature. Both are essential for a healthy environment; their diversity adds beauty and balance in nature. In our blog, we provide a clear difference that removes your confusion about reptiles and amphibians, and you will recognize them clearly.
Learn science online with expert Tutors.
Want to explore more about nature or science topics? Our expert online science tutors are here to help you step by step. They will help you to understand key topics and the natural world easily. Get benefits with our online tutoring service and start learning science, and build strong knowledge for your future.
