Photosynthesis Diagram
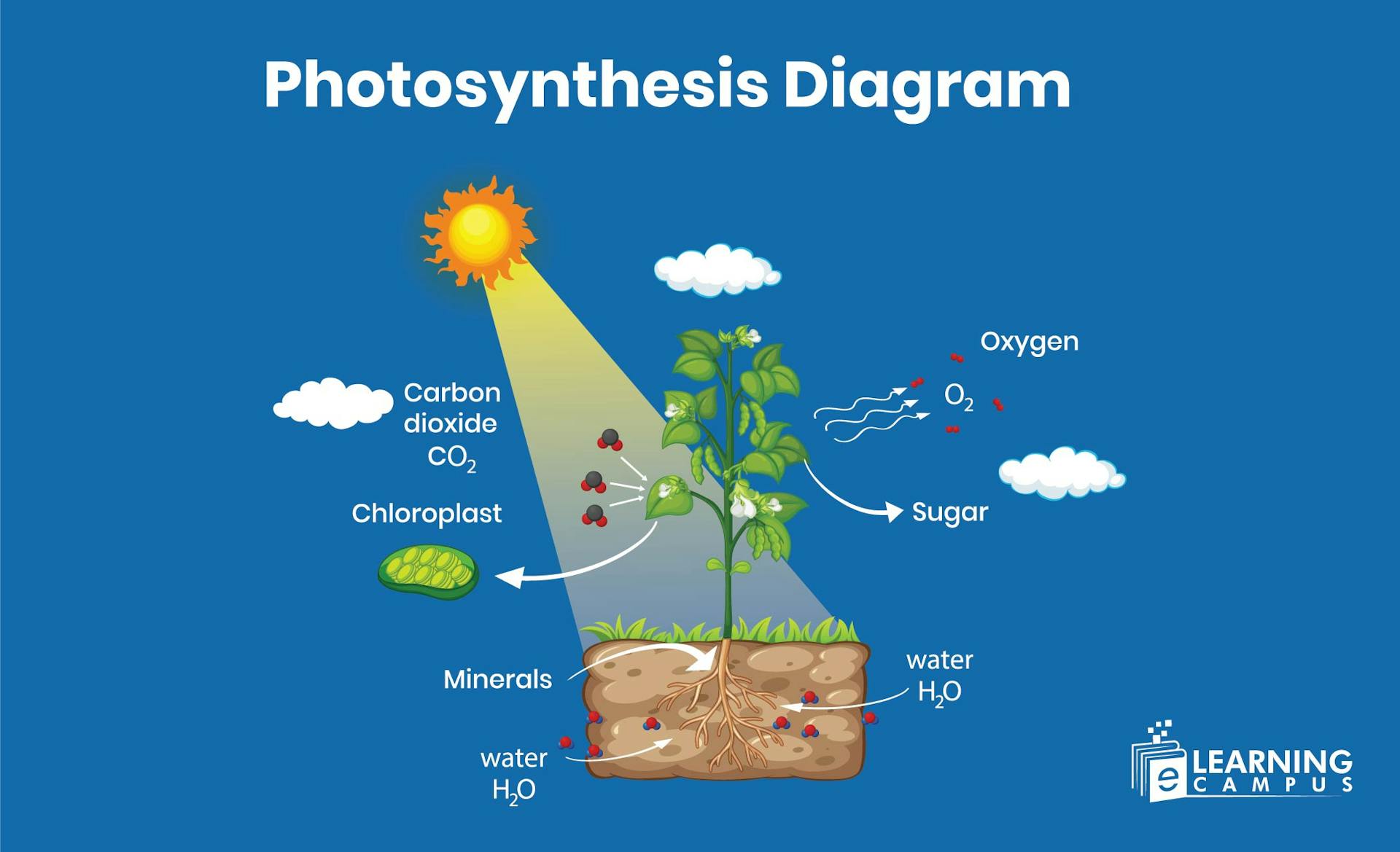
Do you know how plants get energy? Plants get energy through photosynthesis. A photosynthesis diagram illustrates how plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar) and oxygen, a process that occurs within chloroplasts.
In this blog, we will provide a detailed labeled diagram of photosynthesis with its process and steps.
What is Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the biological process by which green plants convert light energy into chemical energy. This energy is stored in the bonds of sugar molecules (carbohydrates) like glucose, which the organism uses for growth and fuel.
This conversion of light energy into chemical energy occurs in chloroplasts, utilizing the green pigment chlorophyll. The chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and reflects green light, making leaves appear green.
Plants need three things to perform photosynthesis:
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
- Sunlight
A labeled photosynthesis diagram is shown below.
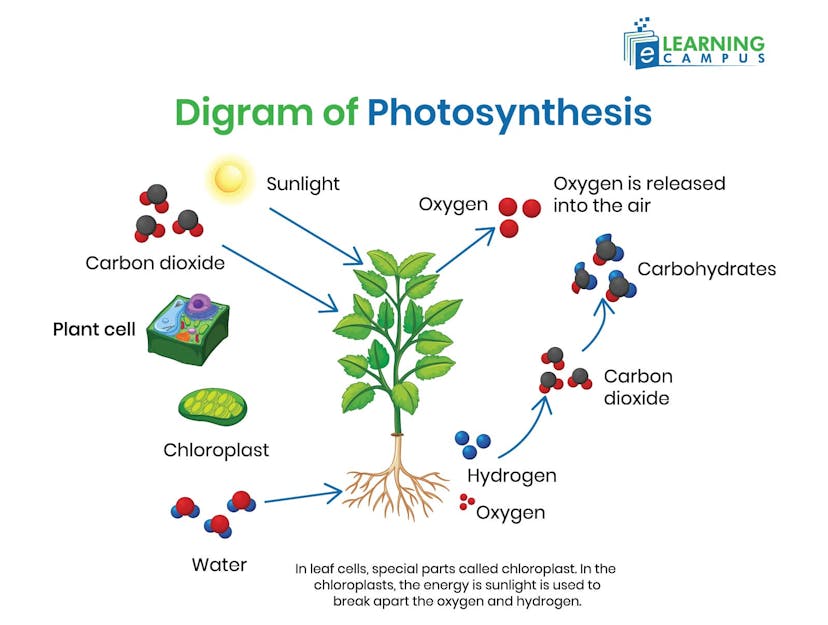
Process of Photosynthesis Explained With Diagram
Photosynthesis is a two-stage process that occurs within the chloroplasts of plant cells. It converts light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
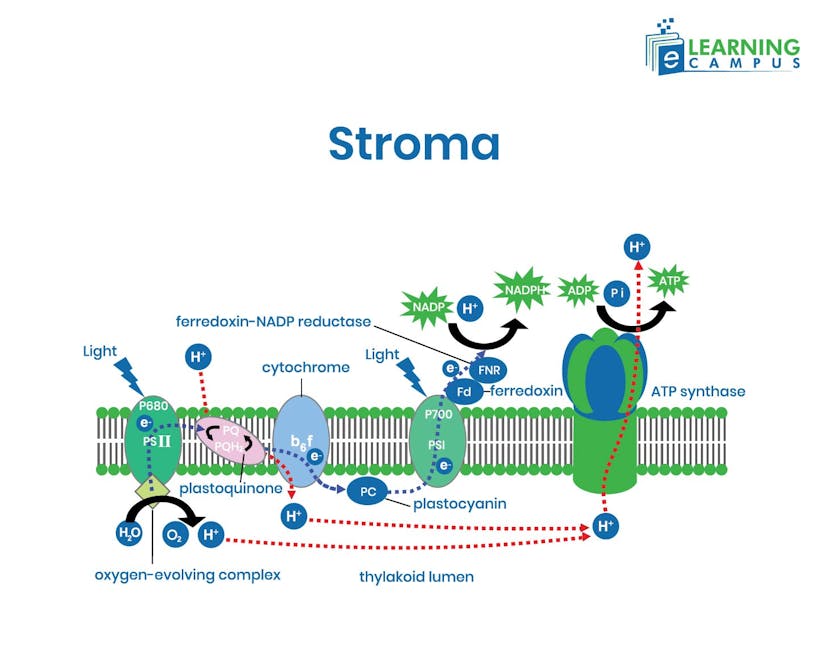
Four major protein complexes in the thylakoid membrane work together in carrying out the light reaction in plants. The proteins include Photosystem II (PSII), Cytochrome b6f complex, Photosystem I (PSI), and ATP synthase.
The overall chemical equation of photosynthesis is given as:
Carbon dioxide + Water + solar energy → Glucose + Oxygen
6CO₂ + 6H₂O ⟶(solar energy) C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Stage 1: Light-Dependent Reactions
These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes and require direct sunlight to function. The stages of light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis include;
- Light Absorption: Chlorophyll (the green pigment) absorbs photons from sunlight. This excites electrons to higher energy levels in Photosystem II (PSII).
- Water Splitting (Photolysis): To replace the lost electrons, Water molecules (H₂O) are split in a process called photolysis. This releases:
Oxygen (O₂): Released into the air as a byproduct.
Hydrogen ions (H⁺): Build up inside the thylakoid.
Electrons: Fed back into the photosystem.
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC): The high-energy electrons travel through a chain of proteins. This movement pumps more H⁺ ions into the thylakoid, creating a concentration gradient.
- ATP Synthesis (Chemiosmosis): H⁺ ions flow back out through an enzyme called ATP synthase. This movement provides the energy to convert ADP into ATP.
- NADPH Formation: At Photosystem I (PSI), electrons are re-energized by light and used to reduce NADP+ into NADPH (an electron carrier).
Below is the detailed diagram of photosynthesis in stage 1.
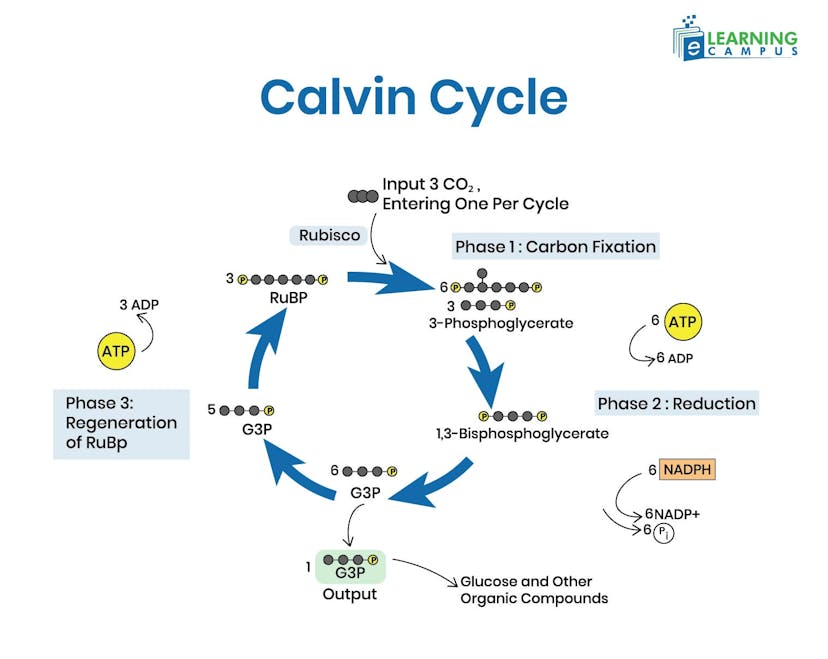
Stage 2: Light-Independent Reactions (The Calvin Cycle)
The light-independent reactions, or Calvin cycle, do not require light directly but use the ATP and NADPH produced in Stage 1. It occurs in the stroma (fluid-filled space) of chloroplasts and consists of three main phases:
Carbon Fixation
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere diffuses into the leaf through stomata and enters the stroma.
- The enzyme RuBisCO (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) catalyzes the attachment of CO₂ to a 5-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).
- This produces an unstable 6-carbon compound that immediately splits into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA), a 3-carbon compound.
For every CO₂ molecule fixed, two 3-PGA molecules are formed.
Reduction
- Each 3-PGA molecule receives a phosphate group from ATP, converting it to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
- NADPH (from the light reactions) donates electrons and hydrogen, reducing 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a 3-carbon sugar
- This is the actual reduction step where CO₂ is converted into a sugar
For every 3 CO₂ molecules fixed, 6 ATP and 6 NADPH are consumed to produce 6 G3P molecules
Regeneration of RuBP
Out of every 6 G3P molecules produced, only 1 G3P exits the cycle to be used for glucose synthesis. The remaining 5 G3P molecules (15 carbons total) undergo a complex series of rearrangements. These reactions use 3 more ATP molecules. The 5 G3P molecules are reorganized to regenerate 3 RuBP molecules (15 carbons), allowing the cycle to continue
Building Glucose
Two G3P molecules (3 carbons each) are combined to form one molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆). This means the cycle must turn 6 times (fixing 6 CO₂) to produce enough G3P for one glucose molecule.
Net equation for one turn (3 CO₂) is
3 CO₂ + 9 ATP + 6 NADPH → 1 G3P + 9 ADP + 8 Pi + 6 NADP⁺
The Calvin Cycle is essentially the process of using chemical energy (ATP) and reducing power (NADPH) from the light reactions to convert inorganic carbon (CO₂) into organic sugar molecules that the plant can use for energy and growth.
Below is a detailed photosynthesis diagram labeled.
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Diagram
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two interconnected biological processes that form a continuous cycle of energy and matter essential for life on Earth. They are essentially chemical opposites, i.e, the products of one process serve as the reactants for the other.
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells (algae/bacteria) using sunlight, water, and CO2 to make food (glucose) and oxygen, while cellular respiration happens in the mitochondria and cytoplasm of all living cells, including plant cells and animal cells.
A labeled photosynthesis and cellular respiration diagram is given below.
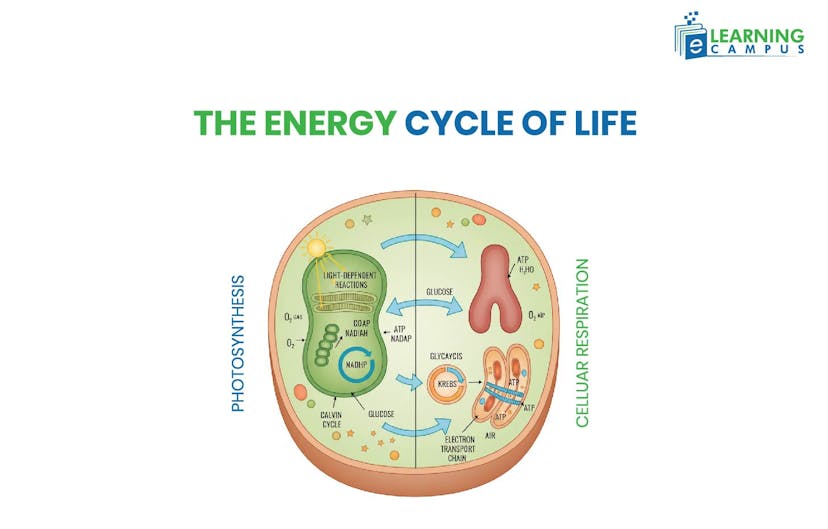
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration: Differences and Similarities
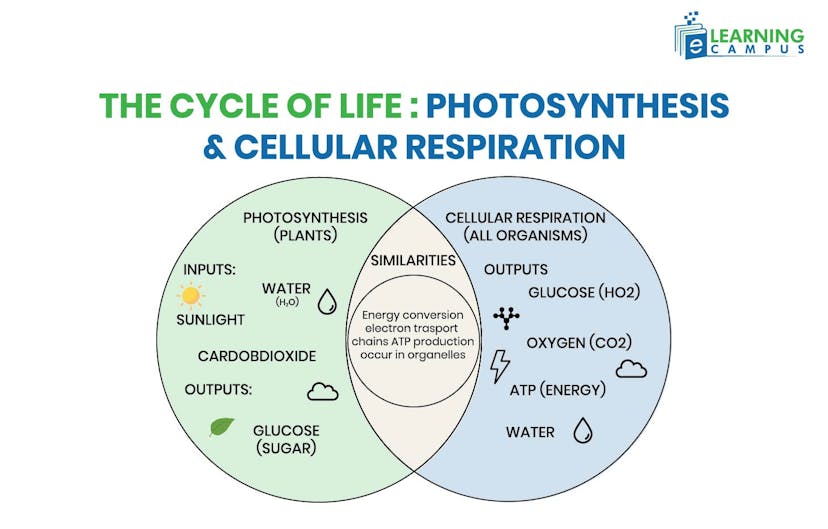
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essentially opposite reactions that complement each other in nature. The products of photosynthesis, such as glucose and oxygen, are the reactants for cellular respiration, while the products of cellular respiration (carbon dioxide and water) are the reactants for photosynthesis.
The similarities between these two processes include;
- Both involve energy transformation. Both processes convert energy from one form to another, though in opposite directions.
- Both occur in organelles with double membranes. Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, while cellular respiration occurs primarily in mitochondria.
- Both use electron transport chains. Each process uses a series of protein complexes to transfer electrons and generate ATP through chemiosmosis
- Both produce ATP. The ATP synthase enzymes in both processes harness proton gradients to synthesize ATP.
- Both involve oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. Electrons are transferred between molecules, with one substance being oxidized and another reduced.
- Both use similar coenzymes. Photosynthesis uses NADPH while respiration uses NADH, both serving as electron carriers.
- Both occur in multiple stages. Each process has distinct phases that work together to complete the overall reaction.
This Venn diagram of photosynthesis and cellular respiration shows the similarities and differences.
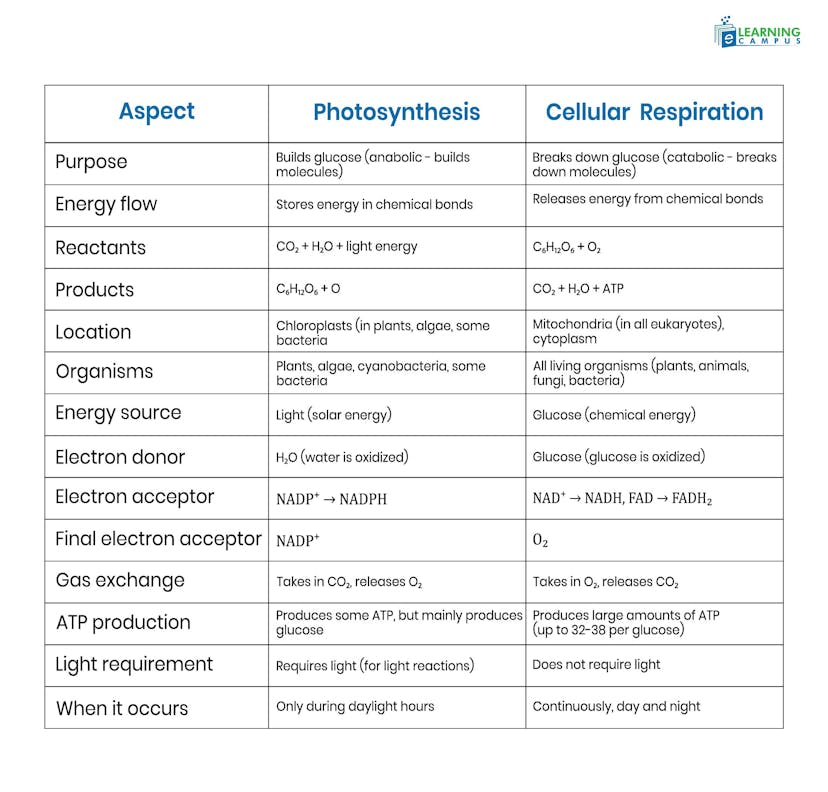
Key Differences between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
There are several differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, as these are opposite reactions.
Conclusion
A Photosynthesis diagram shows plants converting light, water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose (sugar) and oxygen (O2), occurring in chloroplasts. It occurs through two stages, i.e, Light-Dependent Reactions, which take place in thylakoids, using light and water to make ATP, NADPH, and O2, and the Calvin Cycle (in the stroma, using ATP, NADPH, and CO2 to build glucose).
Hire Expert Online Science Tutors
Do you feel learning science is challenging? Join us now. We have expert online science tutors with years of experience in helping students excel in science. You will get individual guidance on the science lesson and exam preparations.
