Animal Cell Diagram| Labeled and Explained

Do you know that the biggest animal in the world, and the smallest insect are composed of the same cell? You may be surprised how an elephant and an ant can have the same structure. Let’s understand it through an animal cell diagram.
In this blog, you will learn about the cell, the parts of animal cell labeled diagram with their functions.
What is an Animal Cell
The cell is the basic unit of animal life. It is eukaryotic (cells with clearly defined nuclei) and composed of a mass of protoplasm enclosed by the cell membrane. The cell contains a spherical nucleus and organelles, which have specific functions and play an important role in maintaining the cell structure.
Animal Cell Labeled Diagram
The animal cell labeled diagram helps you understand the different parts of the cell and their functions.

Parts of an Animal Cell
An animal cell is composed of different parts. Every part has a specific function. The basic parts of an animal cell are the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, centrioles, and vacuoles.
You will understand parts of animal cell in the diagram of animal cell labeled.
Structure and Function of Parts of the Animal Cell
Like all other cells, the animal cell is composed of many parts. The different parts of the animal cell have specific functions that are essential for the functioning and survival of the animal.
The structure and functions of an animal cell with diagram are explained here. You will learn the function of each part in detail.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is the outer layer of the animal cell. It is a thin membrane and is rich in lipids and protein. It is also known as the plasma membrane. The diagram of a labeled animal cell membrane is explained below.
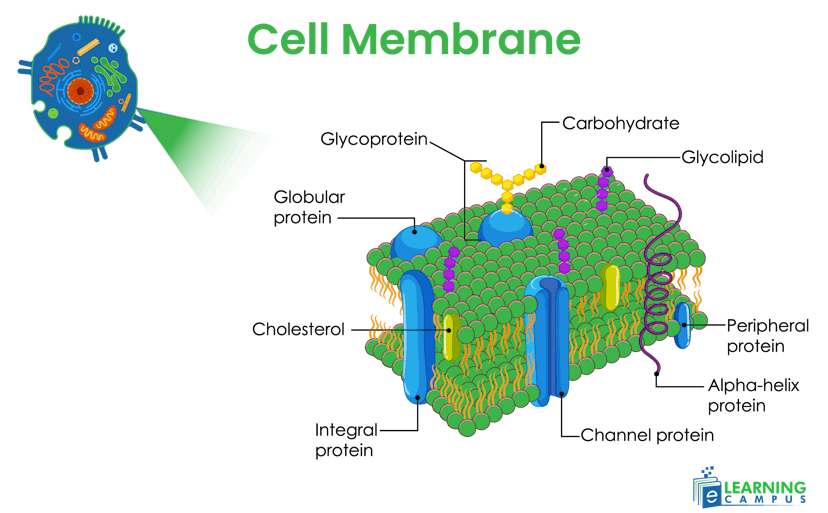
Function
- Maintain the shape and integrity of the cell.
- To protect the cell and the organelles from the surrounding.
- Regulates homeostasis by regulating molecules passing into and out of the cell.
- Facilitates communication among cells.
Nucleus
Every cell contains one nucleus. The nucleus is a spherical organelle located at the center of the cell. A double-layered membrane called a nuclear membrane separates it from the cytoplasm. It also contains organelles such as nucleolus, nucleosomes, and chromatins. The cell nucleus diagram labeled is shown below.
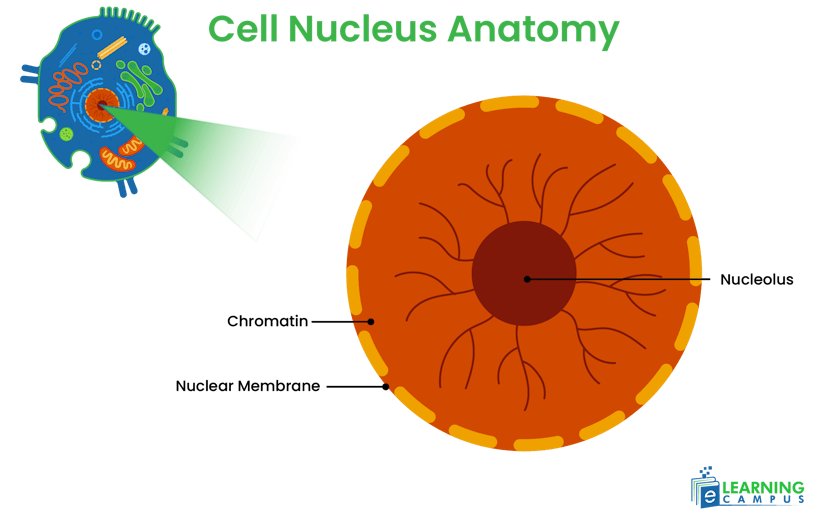
Function
- It contains DNA and hereditary material and has a crucial role in cell division.
- Regulates the cell metabolism.
- The central point for protein synthesis.
- Produces ribosomes.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is a gel-like (semi-fluid) material enclosed in the cell membrane. It is made up of water, salts, and proteins. All the cell organelles are found in the cytoplasm. The labeled picture of an animal cell cytoplasm is given below.
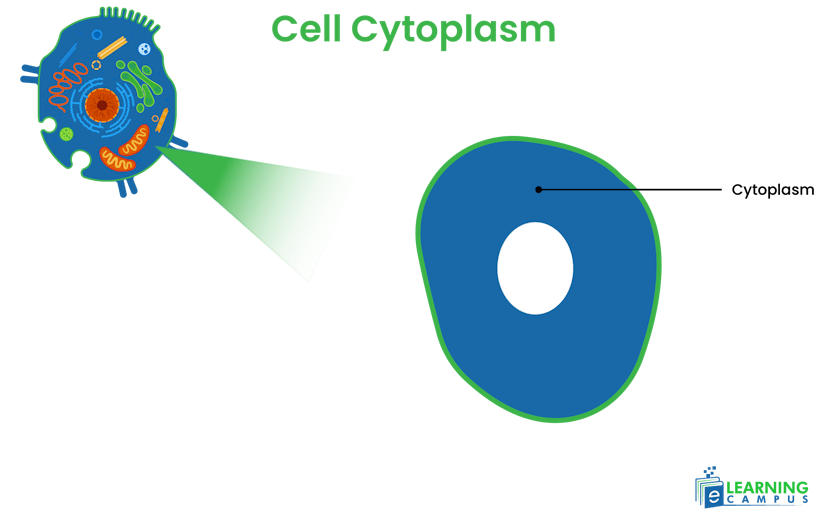
Function
- All the chemical reactions take place in the cytoplasm.
- It helps in the movement and transportation of genetic materials.
- Assists the organelles in functioning properly.
- Cytoplasm provides protection for cell organelles.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, is an organelle bound in a membrane. It has a rod-like structure and is found in the cytoplasm. It is composed of a double membrane, cristae, and matrix. The labeled diagram of an animal cell, the mitochondria is explained below.
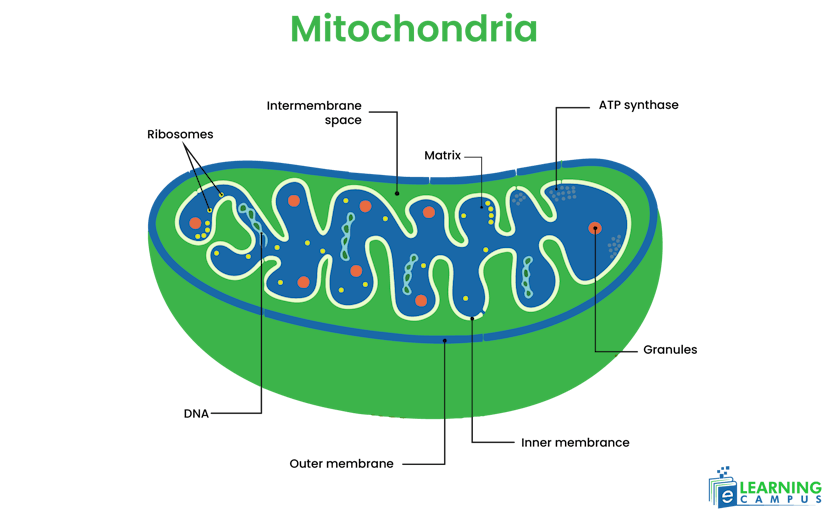
Function
- It produces ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the source of energy of the cell.
- It stores calcium ions essential for body functioning.
- Play an important role in apoptosis (programmed cell death)
- It helps in hemoglobin synthesis.
- The mitochondria have a vital role in the synthesis of amino acids, fatty acids, and phospholipids.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubular membranes. It is found in the cytoplasm, surrounding the nucleus.
Two types of endoplasmic reticulum are found in the cell, Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) and Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). Both have different functions within the cell.
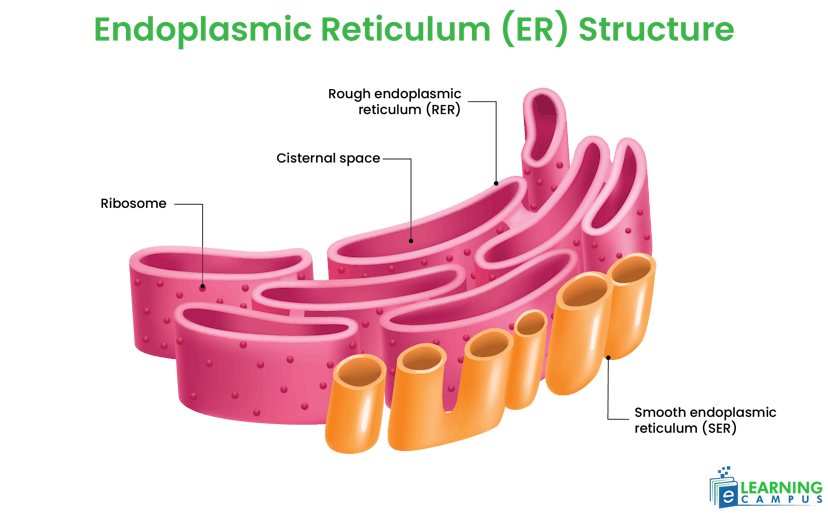
Function
- The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis.
- RER helps in shaping and functioning of proteins.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in synthesis of lipids and steroids.
- SER detoxifies drugs and other harmful substances in the liver.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle composed of cisternae, a series of stacked pouches. These cisternae are layered upon each other to form a Golgi complex.
The labeled picture of an animal cell Golgi apparatus is shown below.
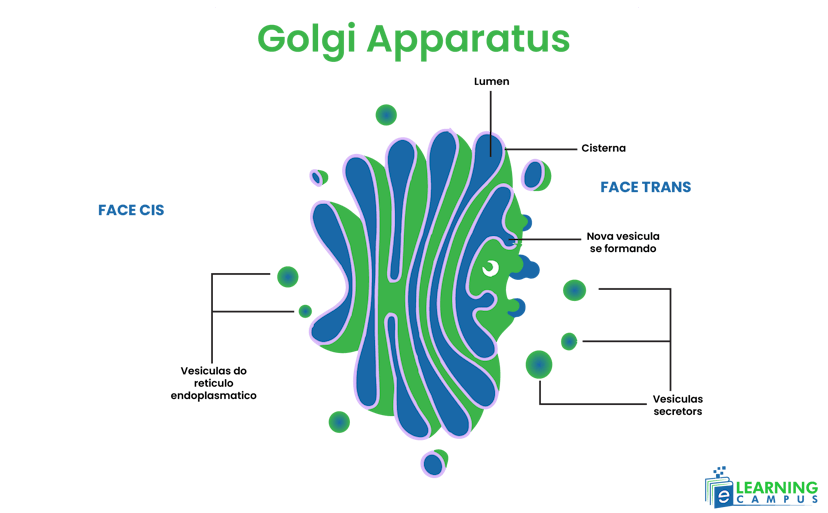
Function
- It is a site for proper structuring and functioning of protein.
- The Golgi apparatus helps in the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
- Assist in root hair formation.
- It helps in membrane recycling and transformation.