Plant Cell Model
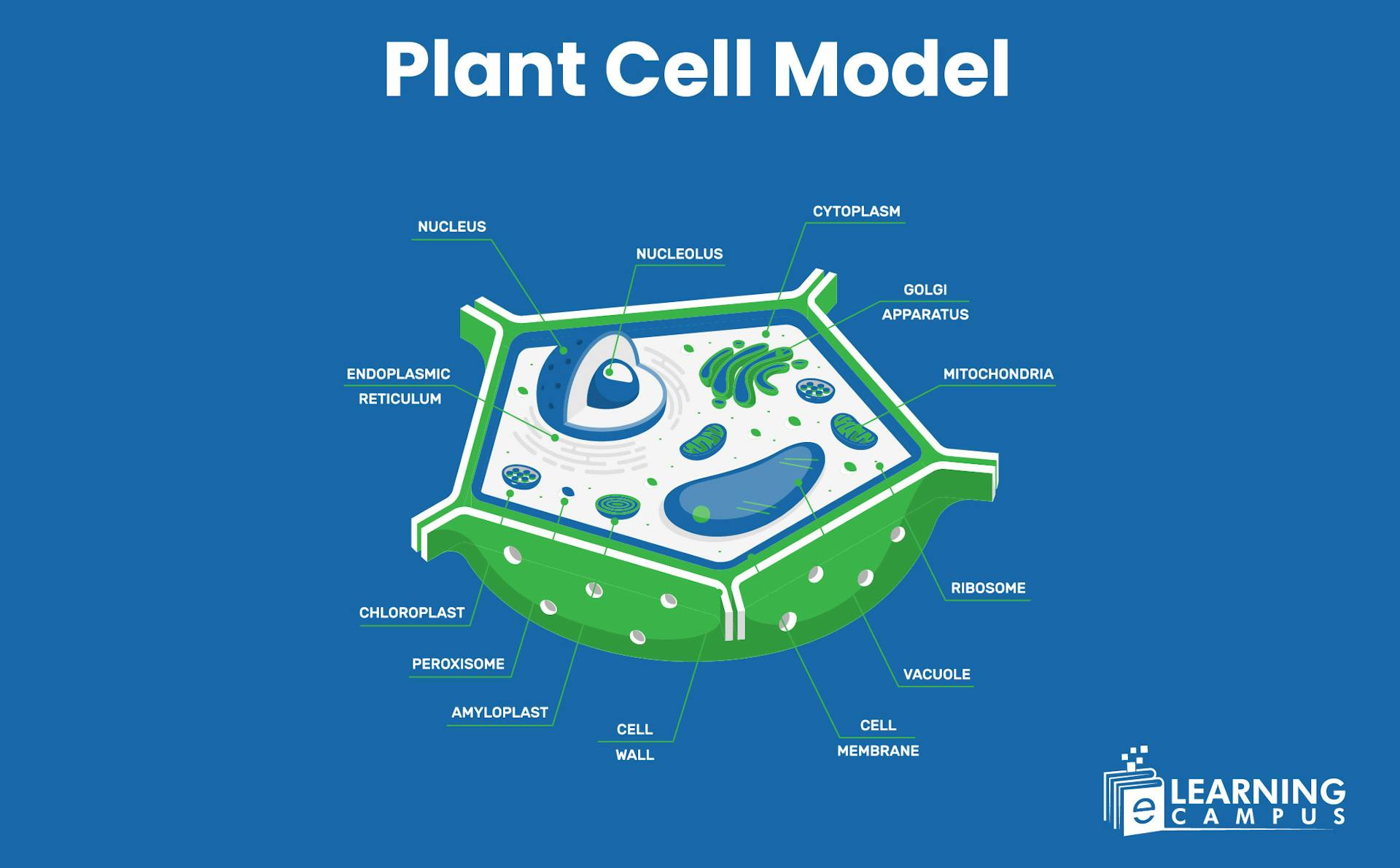
We have been studying plant cells since our primary school years and are familiar with the picture of a plant cell. Learning about the different organelles through a three-dimensional plant cell model provides crystal-clear insight into the structure and function of the cell.
In this blog, you will learn about the plant cell, the cell model of a plant, its organelles, and the function of different parts.
Plant cell
A cell is a primary unit of plants. It is a eukaryotic cell, which means it has a defined nucleus with a visible membrane. The plant cell contains different organelles that have specific functions and play an important role in the maintenance and functioning of the cell. The plant cell contains a cell wall, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus, chloroplasts, and a vacuole.
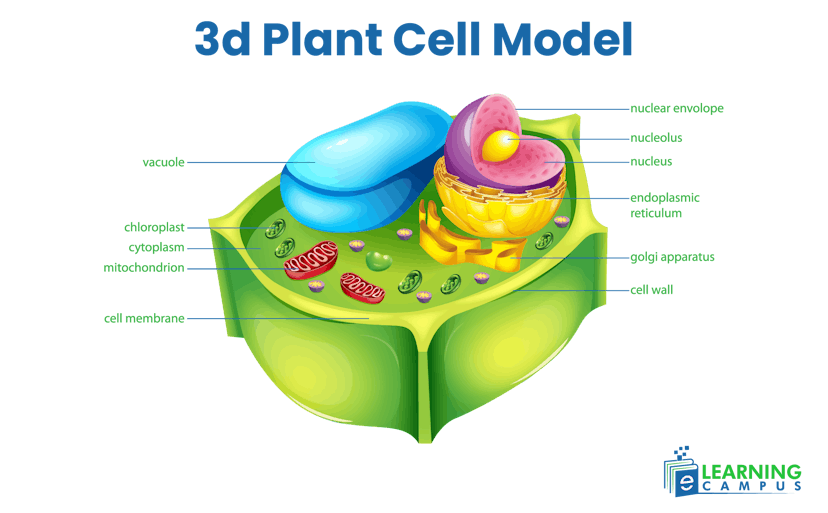
3d Plant Cell Model
A 3d Plant Cell Model is a visual representation of the structure and organelles of a plant cell. This model helps students understand the cell structure unequivocally. The plant cell labelled diagram is shown below.
Functions of Parts of Plant Cell
The different parts of a plant cell have a specific function and they collectively play an important role in the structure and maintenance of the entire cell.
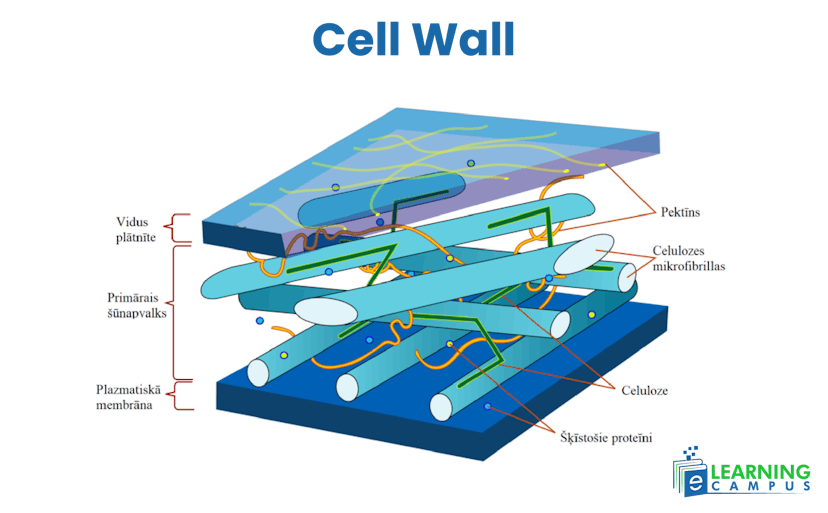
Cell Wall
The cell wall is the outer membrane and is structured with a specialized matrix. The plant cell walls consist mainly of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. It is composed of two layers, i.e, primary cell wall and middle lamina. The basic construction material of the primary cell wall is cellulose.
Function
- Provides mechanical protection to the cell.
- Being semipermeable, it maintains the circulation of essential materials such as water, minerals, and molecular nutrients.
- It also acts as a means of storage for some essential elements.
- It helps the plant to maintain the stiffness and rigidity.
Cell Membrane
Between the cell wall and the cytoplasm, there is a cell membrane also known as the plasma membrane. It is composed of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The main components of the lipid bilayer are phospholipids with cholesterol. Below is given the plant cell diagram labeled.
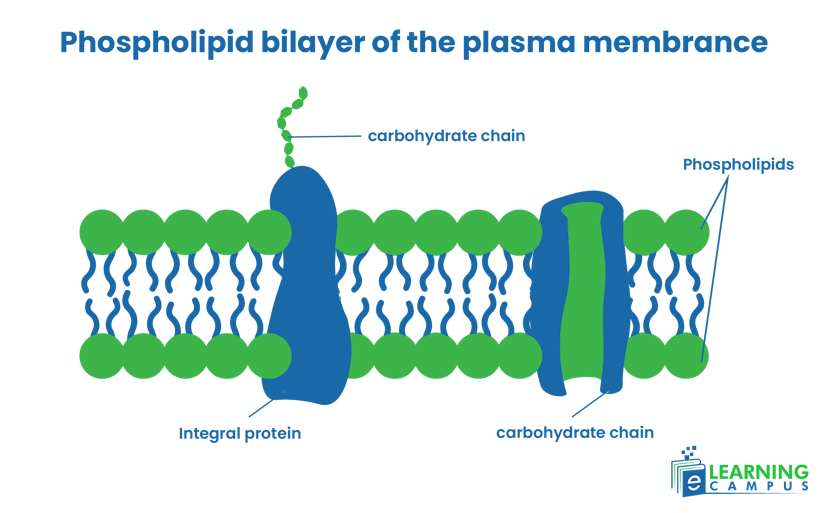
Functions
- Separates cell wall from cytoplasm.
- Regulates the movement of substances within and out of the cell.
- Provide a shield against external damage.
- Helps in the transport of cellular molecules.
Nucleus
The nucleus of a plant cell is a membrane-bound organelle that is present in the cytoplasm. The main parts of the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, and chromatin. The labeled nucleolus of plant cell is shown below.
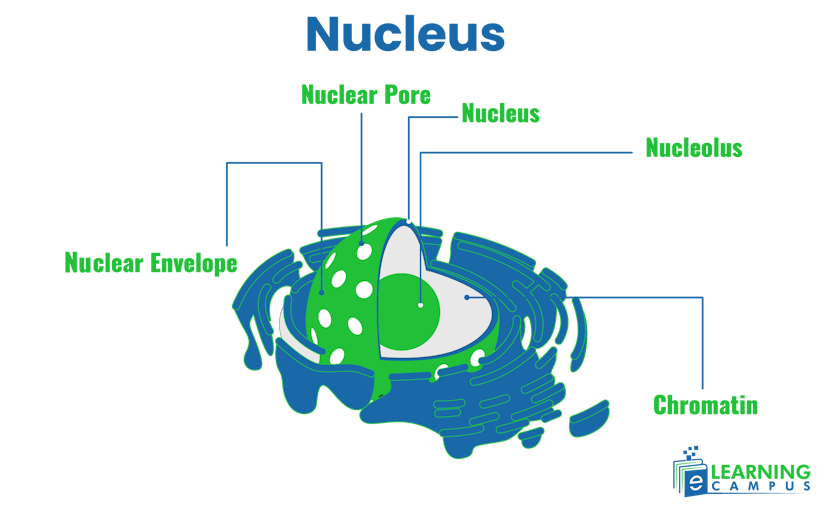
Functions
- It contains genetic or hereditary material.
- Control cellular activities.
- Plays a crucial role in protein synthesis.
- By replicating DNA and organizing ribosomes, the nucleus has an important role in cell division.
Chloroplast
The chloroplast is an organelle in plant cells that carries out photosynthesis and converts the light energy of the sun into chemical energy. It is a double membrane organelle that contains a fluid called the stroma. The stroma is composed of thylakoids that are stacked up to form grana. A labelled plant cell chloroplast is shown here.
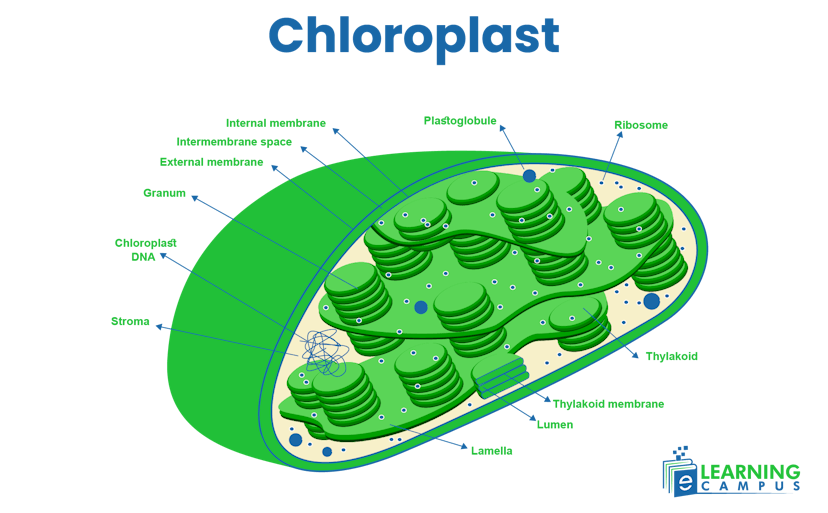
Functions
- It is the central site of photosynthesis.
- It regulates various metabolic processes in plants, including amino acids, hormones, and lipid synthesis.
- In the stroma, during the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide is converted into glucose.
- The chloroplast is responsible for releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
Vacuole
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of the cell. These are vesicles filled with fluid. Vacuoles are also found in animal cell, but plant cell vacuoles are larger than animal cell vacuoles. The membrane around the vacuole is known as the Tonoplast. The inner part of the vacuole is filled with fluid called cell sap. The vacuole in a plant cell labelled diagram is shown below.
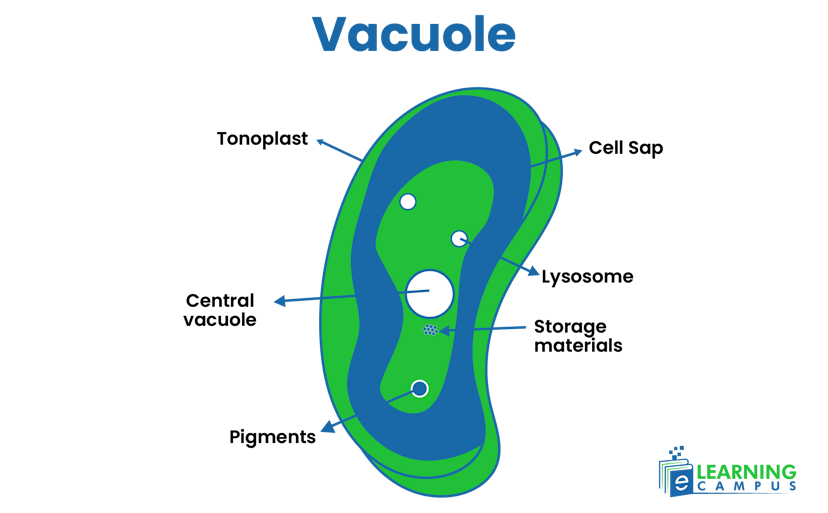
Function
- It stores water, sugars, enzymes, pigments, inorganic salts, alkaloids, and waste products.
- It regulates the turgor pressure of plant cells.
- It plays a crucial role in cell enlargement and growth during plant growth.
- It balances the pH within the cell.
- It helps to dispose of the harmful toxins from the cell.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. The mitochondria in plant cells are a double-layered, spherical oval organelle. The inner membrane of mitochondria has many folds known as cristae. Within the cristae, a fluid is found called the matrix. The labeled diagram of the mitochondria in plant cell is elaborated here.
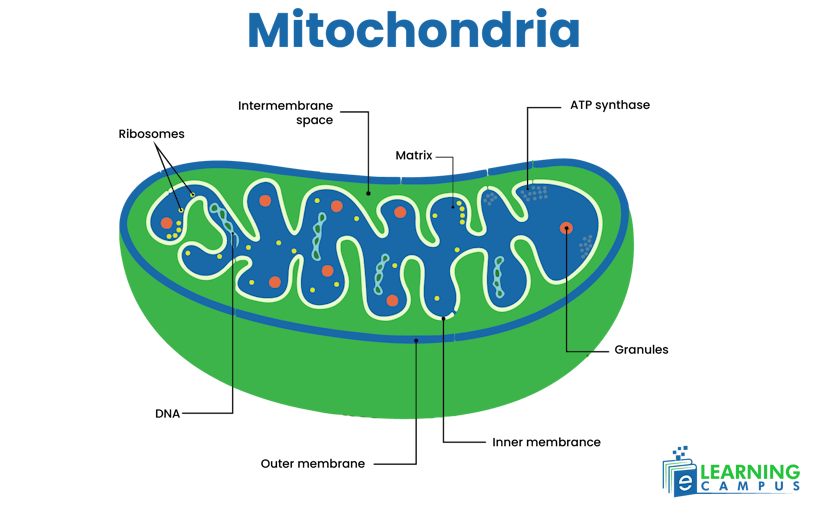
The Mitochondria Function in Plant Cell
- Generates energy to be used by the cell.
- It acts as the means of calcium storage, crucial for signaling activities, cell growth, and division.
- Releases certain proteins to regulate apoptosis.