What is Newton's First Law
Have you ever wondered why rolling balls stop after some time or why you lean forward when the bus suddenly brakes? These moments are explained by Newton’s first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia. This simple law helps us understand how objects behave when no force is acting on them.
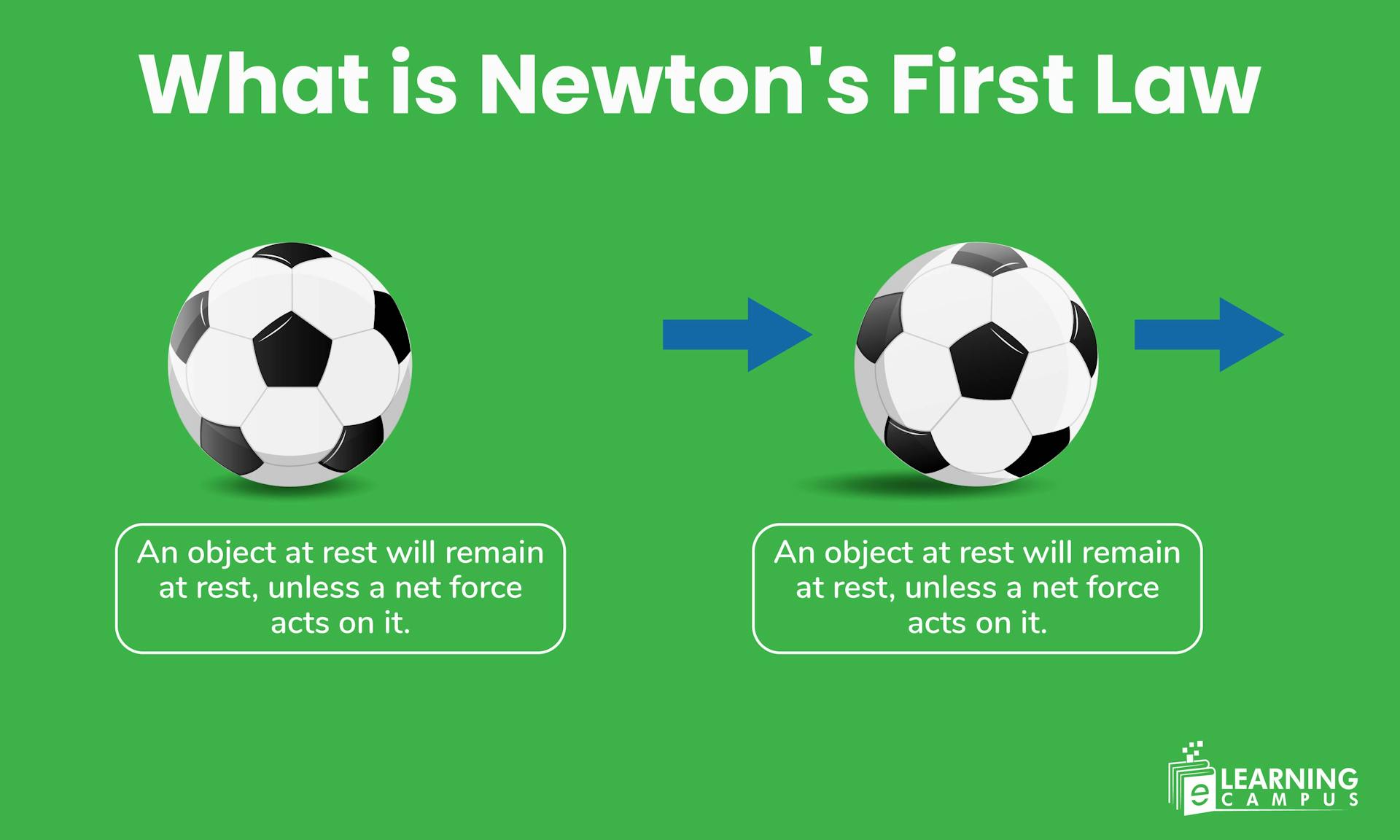
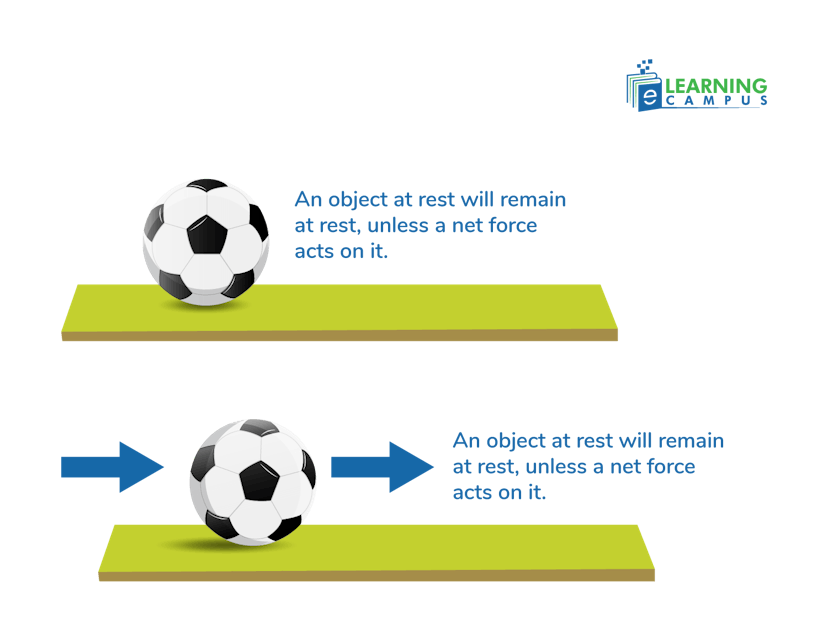
Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line unless acted upon by any external force.
In this blog, we will provide a complete guide on Newton's first law and how it is related to inertia with real-life examples.
Introduction
Issac Newton (1642-1727) was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and one of the most influential scientists in history. He is best known for discovering the three laws of motion. These laws are the foundation of physics, and he also explained the law of universal gravitation, which explains how objects move and how gravity works. Their invention has great contribution to the field of physics. Here’s how;
- He laid the foundation for modern physics.
- He changed the way we understand the universe.
- His laws are still used in engineering, space science, and everyday technology.
What is Newton's First Law?
Newton's first law, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object will remain at rest or continue moving at a constant speed in a straight line unless an external force acts on it.
Newton's First Law of Motion states:
An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force.
Newton's first law and Inertia?
Newton's first law is also called the law of inertia. Inertia is a tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion. If no net force acts on an object, then the object will maintain its constant speed. Objects with greater mass have more inertia, so they are harder to move or stop.
- More mass =more inertia
- Less mass = less inertia
- The law of inertia is another name for Newton's first law. It states that:
“An object will remain at rest or continue moving uniformly in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force”.
For Example
- When the driver suddenly applies the brakes, and the car stops suddenly, your body moves forward due to inertia.
- A body stays still until someone kicks it.
- A ball on the ground eventually stops because friction slows it down.
- A book on a table stays still until someone pushes it.
Why Newton's first law is Important
Newton's first law of motion is important because it helps us understand how objects behave in everyday life and in science. Here’s why:
- It is the foundation of physics and forms the base of Newton's other laws of motion.
- It introduces the concept of inertia, showing that objects resist changes in their motion. Without this understanding, predicting how objects move would be impossible.
- It shows how objects behave when forces act or don't act on them.
- It explains why seat belts, helmets, and brakes are necessary.
- It helps design vehicles, machines, and tools safely that handle forces properly.
Real Life Examples of Newton's First Law
Real-life examples provide a clearer understanding of the first law of motion. Here are some examples:
- Seatbelts in cars
Your body continues moving forward when a car stops suddenly. The seatbelt applies the force needed to stop your motion safely.
- A coin trick
A coin on a card drops into a glass when a card is flicked. The coin stays still because of inertia.
- A moving car
When a car suddenly stops, passengers fall forward. This happens because their bodies want to continue moving at the same speed due to inertia.
Conclusions
Newton's first law, also called the law of inertia, is one of the most powerful principles in physics. It teaches us that motion does not change without cause. An object stays at rest or keeps moving in a straight line unless a force interferes. By observing objects around us, we can clearly see that inertia is always at work, the movement of everything in our environment.
Learn Science online with expert Tutors.
Discover the power of inertia, or want to explore more on Newton's first law? Don't worry, our expert online science tutors can help you. Learn how the first law of motion works and strengthen your understanding of physics. Get benefits from our online tutoring service and start studying now to be fully prepared for your test or exams.
