Force and Motion
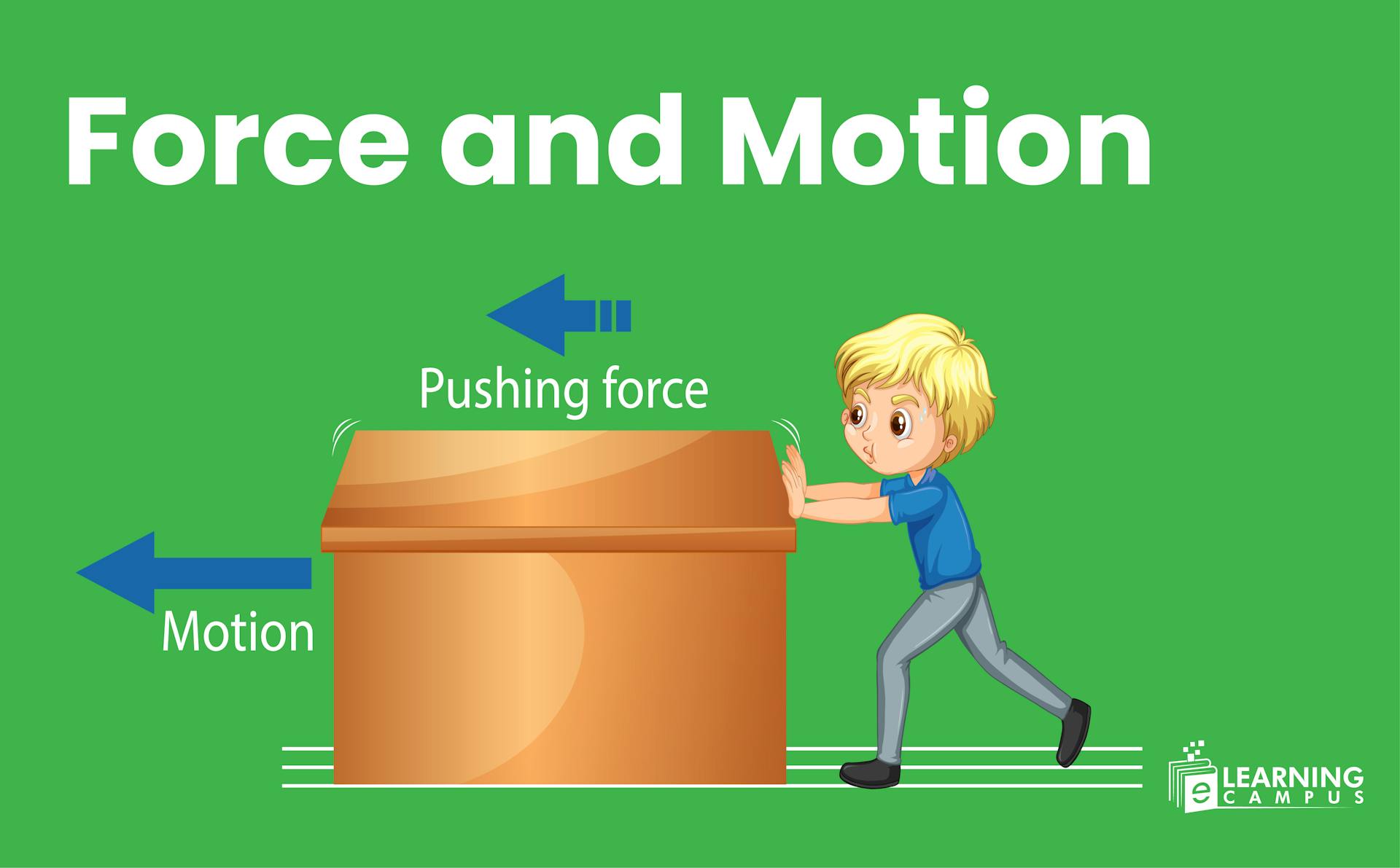
The force and motion are two important, intrinsically linked natural phenomena. Force is an agent that causes a change in the motion of an object. The relation of force and motion can be deliberately explained with the help of Newton’s laws of motion, especially Newton’s second law of motion.
In this blog, you will learn about force and motion and the relationship between force and motion. Let’s first learn the forces and motion basics.
Force
A force is a push or pull on an object that can cause it to change its motion or changes its shape. It is an interaction between objects that can change their state of rest or motion. A force is an external agent that acts on a body and changes its state from rest to motion and vice versa.
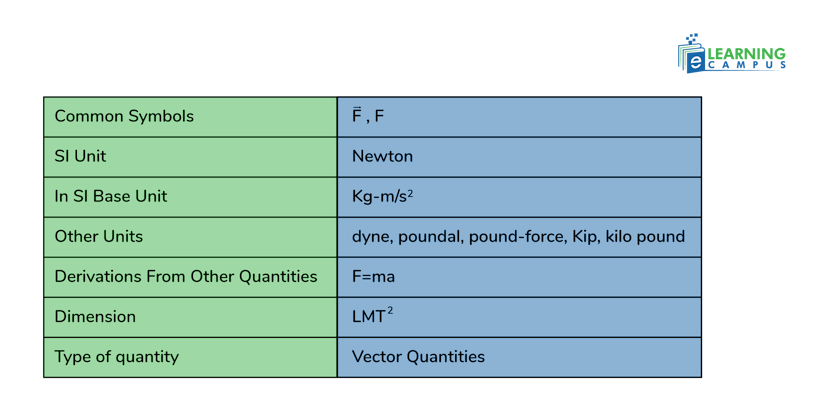
The force is measured in Newtons. The basic details about the force are given in the table below.
Effects of Force
Force is an agent of change, either in the direction or speed of a thing. When a force is applied to a certain object, there is a certain change. The effects of force can vary.
Force can move a stationary object
Force is an agent that can cause motion in stationary objects. When a certain quantity of force is applied to an object at rest, it will start to move. For example, a ball is on the table, and if we apply a force to it, it will start moving.
The magnitude of movement will depend on the force applied.
Slows down or stops the object
A force can slow down the speed of a moving body or stop it altogether. If a force is applied in the direction opposite to the motion of a body, it will slow down. For example, if we pull a moving cycle from behind, it will slow down and stop eventually.
Force Causes Moving Object to Move Faster
A force exhibits the property of increasing the speed of a moving body. If a force is applied to a moving body, it will cause it to move faster. For example, if a footballer hits the moving ball, the ball will start moving faster.
Force can Change the Direction of Objects
A force has the ability to change the direction of an object. For example, when a bowler throws the ball towards a batsman, he hits the ball and changes its direction.
Change the shape of objects
When a force is applied to an object, it can change its shape. When a spring is pulled with a force, it gets stretched and changes its shape.
Motion
Motion is defined as the act or process of changing the place or position of an object with respect to time. Motion is measured and observed with the point of reference. For example, a man sitting in an airplane is in motion with reference to people on Earth. The man is at rest with reference to the passengers inside the plane.
Relationship Between Force and Motion
Force and motion are intimately related. Force is the cause of motion, and motion is a result of force. Newton's Second Law of Motion describes this relationship mathematically. It shows that a net force applied to an object will cause it to accelerate. This acceleration can result in changes in speed, direction, or even a change from a state of rest to motion.
Let’s look deep into the relationship between motion and force with the help of Newton’s law of motion.
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws are essential for understanding the movement of objects in various situations.
Newton’s first law of motion
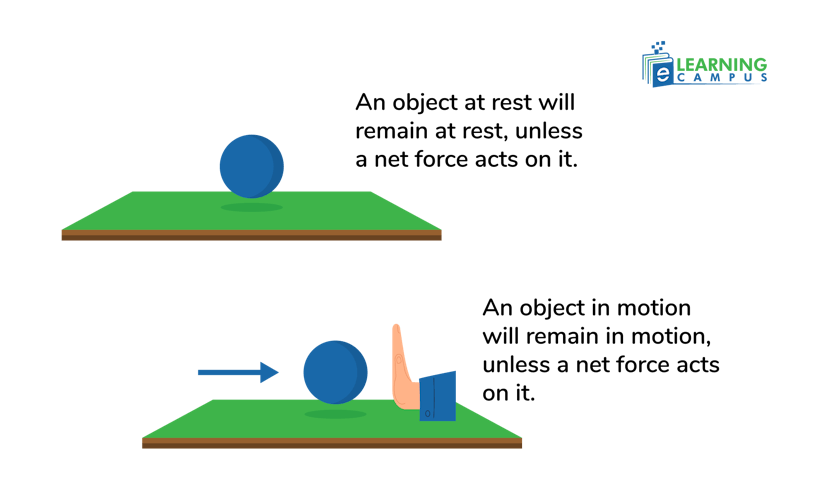
Newton’s first law of motion is also known as the law of inertia. It states that ‘an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed in the same direction unless an external force acts upon it’.
For example, a ball on the table will stay at rest until an external force is applied to it, which makes it move. In the same way, the ball will keep moving until a force is applied to stop it.
Newton's second law of motion
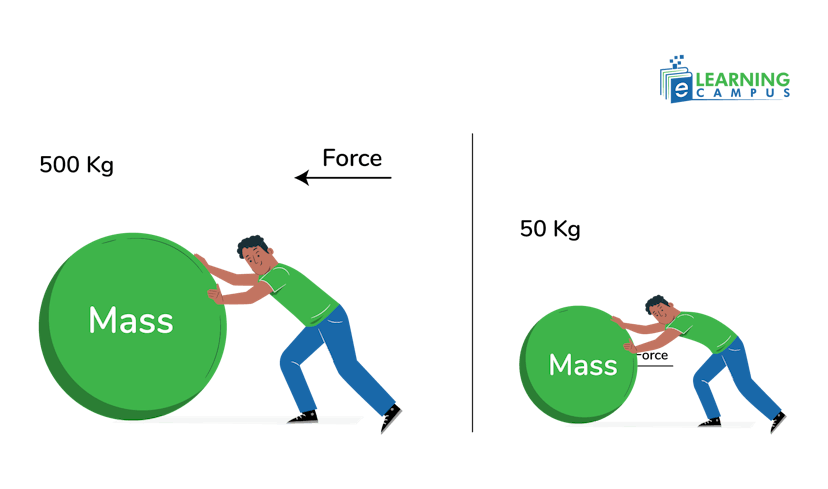
Newton’s second law of motion mathematically represents the relation between motion and force. It states that ‘when a net force is applied to an object, an acceleration is produced. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.’
It means that the more the force, the more will be the acceleration, and the bigger the mass, the smaller is acceleration.
Let’s look at it mathematically.
If we apply a force ‘F’ to an object with mass ‘m’, an acceleration ‘a’ will be produced.
The acceleration is directly proportional to force,
a∝ F
The acceleration is inversely proportional to mass,
a∝ 1m
Combining both equations.
a∝ Fm
a=Fm
This equation can also be written as;
F=ma
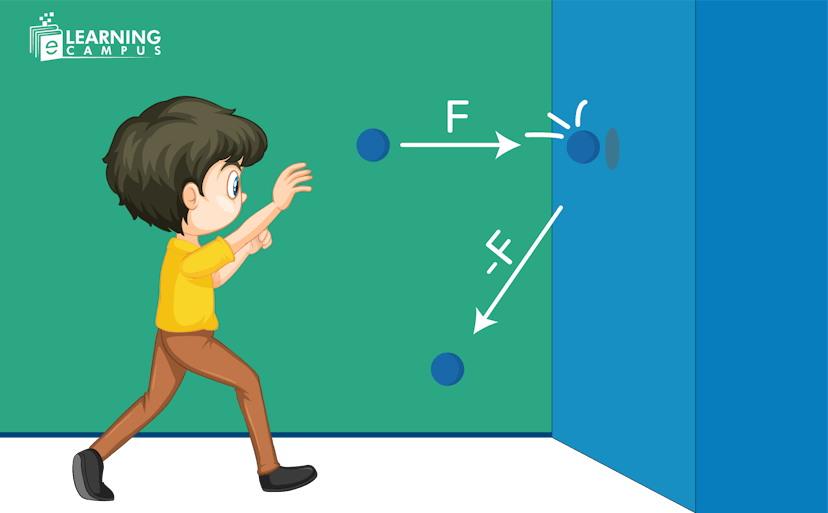
Newton's third law of motion
Newton's third law of motion states that ‘for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force.’ This means that when one object exerts a force on another, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force back on the first object.
For example, if a person hits a wall with a cricket ball, it acts on the wall by applying a force. At the same time, the wall also exerts the same magnitude of force on the ball, but opposite in direction.
It is represented as;
F=-F
Conclusion
Force and Motion are considered two sides of a coin. They are intrinsically linked, and their relation can be described mathematically with the help of Newton’s laws of motion. In a nutshell, force is an agent that causes motion in an object, and motion is the result of any unequal force applied to an object.
Learn Physics online
Are you looking for an online tutor to learn physics in a fun way? Let us help you. We have professional online science tutors to make physics easy to understand. You will learn the concepts and apply them in the real world.
