Derivatives of Inverse Trig Functions
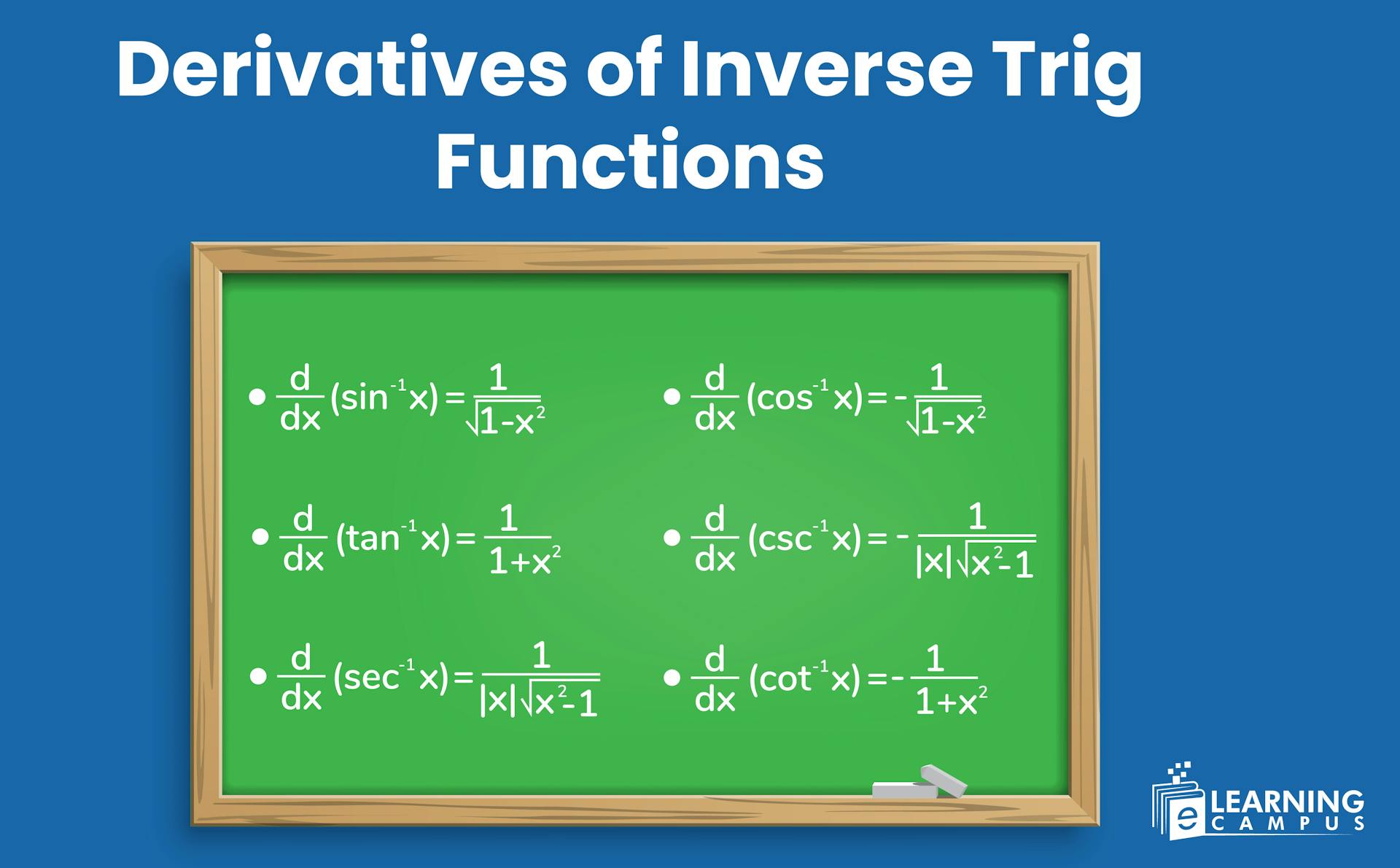

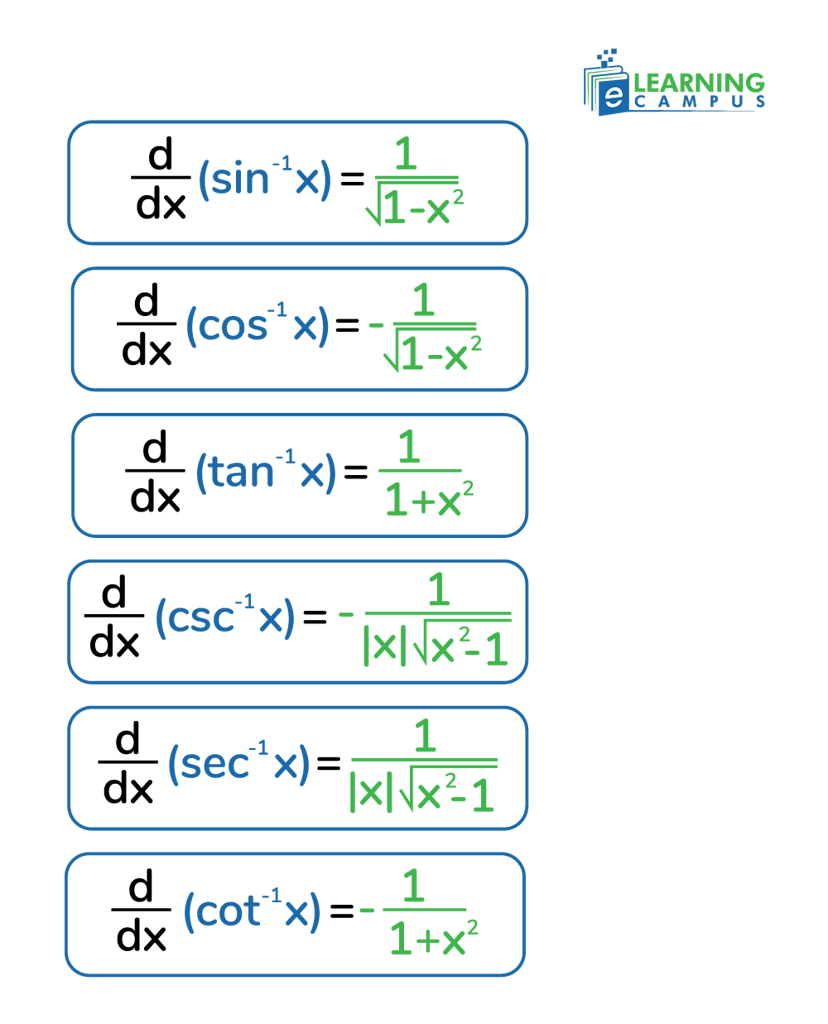
The derivatives of inverse trig functions are the derivatives of the inverse of basic trigonometric ratios such as sin, cos, and tan. The derivative of an inverse trig function represents the instantaneous rate of change of the inverse function for its input. The derivatives inverse functions are not trigonometric functions themselves, but rather algebraic functions involving square roots and powers of the input.
Let’s first understand the inverse trigonometric functions.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Inverse trigonometric functions, also known as arc functions, are the inverses of the standard trigonometric ratios like sine, cosine, and tangent. They are used to find an angle when a trigonometric ratio is known. These inverse ratios are represented as;
The inverse trig derivatives, also known as the arc derivatives, can be defined as the derivatives of the inverse of trigonometric functions. The implicit differentiation of trig functions is used to find the derivatives of inverse trigonometric ratios.
There are six inverse trigonometric ratios. Differentiation is helpful in finding the derivatives of inverse trig functions. Derivatives show the rate of change of a function with the change of a variable. The derivatives of inverse trig functions are represented as;
We can find the derivative of inverse trigonometric functions using the implicit differentiation of trigonometric functions method. Let us look at the proof of derivative of inverse trig functions.
To find the derivative of Arcsin (sin-1), consider that
Differentiating on both sides with respect to x
The trigonometric identity shows that,
From the above equation, we can find that;
Substituting this value in equation (i)
To find the derivative of cos-1, let us consider
Differentiating both sides w.r.t x, we have,
The Pythagoras identity states that;
From the above equation, we can calculate that;
Substituting the value of sin y in equation (i),
So, the derivative of cos-1x, arccos x, or inverse cos x is
The derivtive of arctan can be found by assuming
Differentiating both sides w.r.t x
The trigonometric identity shows that;
From the above equation, we can find that;
Substituting the value of sec2y in the equation (i).
So, the derivative of tan-1x or inverse tan x is 11+x2.
To find the Derivative of Arccsc, let us assume that
Differentiating on both sides w.r.t x,
One of the trigonometric identities shows that;
From the above equation, we can find;
Substituting the value in equation (i)
The derivative of Arcsec (sec-1) can be found by assuming
Differentiating both sides w.r.t x
The trigonometric identity shows that;
Substituting the value in equation (i)
To find the derivative of
let us assume that
Then,
Differentiating both sides w.r.t x.
One of the trigonometric identities states that;
By substituting the value in equation (i)
So, the derivative of
Conclusion
The derivatives of inverse trig functions refer to the process of differentiating the inverse trig ratios to find their derivatives. The easiest method to find the derivatives is implicit differentiation of trigonometric functions.
Are you struggling with math? Don’t worry. We have expert online math tutors to make math fun for you. You will get personalized instruction according to your needs.
