Classification of Living Things
Do you know that there are 8.7 million species of living organisms on Earth? Humans are one of them. To study this huge number of species, the system of classification of living things has been introduced.
Living things are classified into a hierarchical system of groups. It starts with broad categories like domains and kingdoms, and becomes more specific with phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and finally, species.
What Does the Classification of Living Organisms Mean
The classification of living organisms refers to the method of grouping organisms together according to their evolutionary history and similar characteristics.
The science of the classification of living things is also known as taxonomy or biological classification.
What Are the Bases of the Classification of Living Things
Living things are classified based on different features and characteristics. It is primarily based on evolutionary relationships characterized by similarities in their physical characteristics, genetic makeup, and other biological features.
The key features on which organisms are classified include;
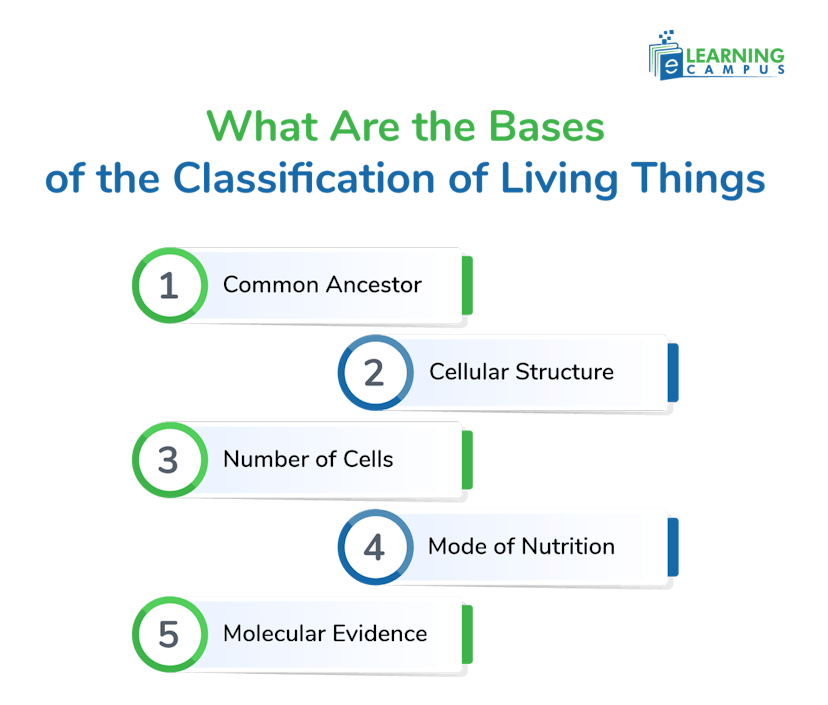
Common Ancestor
The most fundamental basis for the classification of species is the idea that all living organisms share a common ancestor. This ancestor is referred to as the last universal common ancestor (LUCA). It is the hypothetical unicellular organism from which all life on Earth is believed to have diverged.
Cellular Structure
The living organisms are classified based on the structure of the cell. On the basis of cellular structure, living things are divided into two categories, i.e, Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic. Eukaryotes are organisms with a nucleus in the cell, while Prokaryotes are without a nucleus.
Number of Cells
Organisms are also grouped based on the number of cells. Living organisms that fall into this trait are Unicellular and multicellular. The unicellular organisms are composed of only one cell, while multicellular organisms have several cells.
Mode of Nutrition
The mode of nutrition is a key aspect of classifying living things. An organism may be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. Autotrophs produce their own food, like plants. Heterotrophs obtain food from other sources, such as plants.
Molecular Evidence
The modern biological classification relies on molecular evidence, such as DNA and protein sequences. It helps to determine the evolutionary relationships of different organisms.
History of Classifying Living Things
The concept of classifying living organisms has evolved over the centuries. From the simple observation-based systems to complex and scientifically driven classifications, the mechanism of classification has changed over time.
Aristotle’s Classification
Aristotle is a well-known philosopher to developed the first classification systems of living things. He categorizes organisms into two kingdoms, i.e, plants and animals.
He further divided animals and plants based on habitat and physical characteristics, size, and structure.
- Plants: The plants are divided into Herbs, shrubs, and trees.
- Animals: Animals are categorized as land-based, water-based, and air-based.
The Linnaean System of Classification
Carl Linnaeus, a Swedish botanist, introduced the classification based on the binomial nomenclature and a hierarchical system of ranks. This system classifies species based on shared characteristics through ranked categories. It ranges from broad to specific.
The key features of the Linnaean classification system include;
Hierarchical Structure: This classification system is built on a hierarchy of taxa. It starts with broad categories like kingdom and becomes more specific as we move down the classification.
Taxonomic Levels: The taxonomic levels in the Linnaean system are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. The modern system of classification includes the domain as the broadest level.
Binomial Nomenclature: In this system, each species is given a unique scientific name. The name consists of its genus and species. For example, Homo sapiens is for humans. In Homo Sapiens, Homo is the genus name and sapiens is the species name.
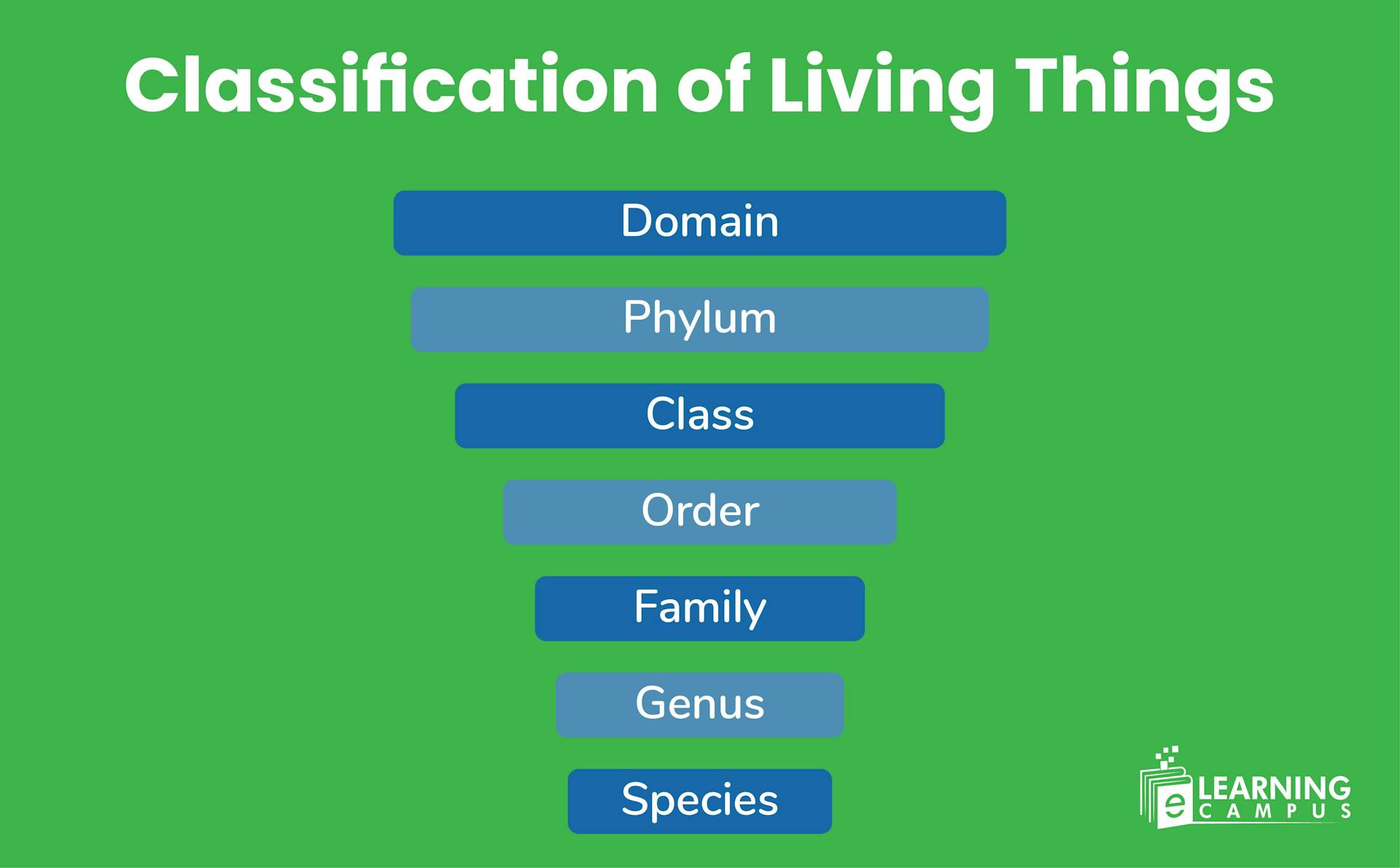
Taxonomic Levels of Classification
The taxonomic levels of classification are a hierarchical system used to categorize and organize all living organisms. This system ranges from a broader category to a specific one.
There are 8 levels of classifying organisms in taxonomy. Each level of the classification represents a group of organisms that have certain similar characteristics and are related through evolutionary history.

Domain
The domain is the highest level of classification of living organisms. It includes all types of organisms. Under the domain, organisms are divided into three categories.
- Bacteria: This domain consists of all prokaryotic organisms, such as eubacteria and cyanobacteria.
- Archaea: It consists of single-celled prokaryotic organisms, such as thermophiles. These are distinct from bacteria despite their similar microscopic appearance.
- Eukarya: It consists of organisms with a nucleus in the cell. For example, plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Kingdom
The kingdom is the second-highest level of classification of living organisms. Organisms in the kingdom are categorized based on the cell type, level of organization, and mode of nutrition.
The kingdom is further divided into;
- Animalia: It includes multicelled and heterotrophic organisms that get their food from other organisms.
- Plantae: it includes multicellular and autotrophic organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- Fungi: The fungi include heterotrophic organisms that obtain nutrients by absorption.
- Protista: includes a group of unicellular eukaryotic organisms, such as algae, protozoa.
- Monera: includes unicellular prokaryotic organisms, such as Bacteria.
Phylum (Division)
A phylum falls under the kingdom in the taxonomical classification of organisms. It groups organisms based on morphological features, structural, or evolutionary relationships. Phylum is used to represent animals, while Division is used for plants.
The phylum examples include Chordata, Mollusca, and Arthropoda.
Class
A class is a group of organisms within a phylum that is categorized based on more specific traits. For example, Mammalia within Chordata. In simpler terms, it is a group of related orders.
Order
Order comes after class within the taxonomical order of classification of living organisms. Each order contains families of organisms with more specific similarities. It is a group of related families.
For example, within the class Mammalia, we have orders like Primates that include humans, monkeys, and apes. Carnivora includes cats, dogs, and bears, and Cetacea includes whales and dolphins.
Family
A family is a taxonomic rank within the hierarchical system of biological classification in which organisms are grouped that are more closely related than those in other families. It is a group of related genera.
For example, the family Canidae includes dogs, wolves, and foxes. All of these organisms share certain characteristics and are more closely related to each other.
Genus
A genus is a group of closely related species. It groups species that share many characteristics and are believed to be closely related through evolution.
The genus Panthera includes lions (Panthera leo), tigers (Panthera tigris), and leopards (Panthera pardus)
Species
Species is the most specific level of the biological classification of organisms. It represents a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
For example, humans (Homo sapiens), domestic cats (Felis catus), and various plants like mango (Mangifera indica).
Conclusion
Living things are classified into a hierarchical system of groups, from broad to specific, to understand their relationships. This system uses eight levels of classification, including domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
Learn Biology Online With Us
Are you struggling with biology and don’t know how to prepare for your exams? Don’t worry. We have expert online science tutors to make the subject easy to understand. You will get a targeted guide for your exam preparations.
