Five Kingdoms System
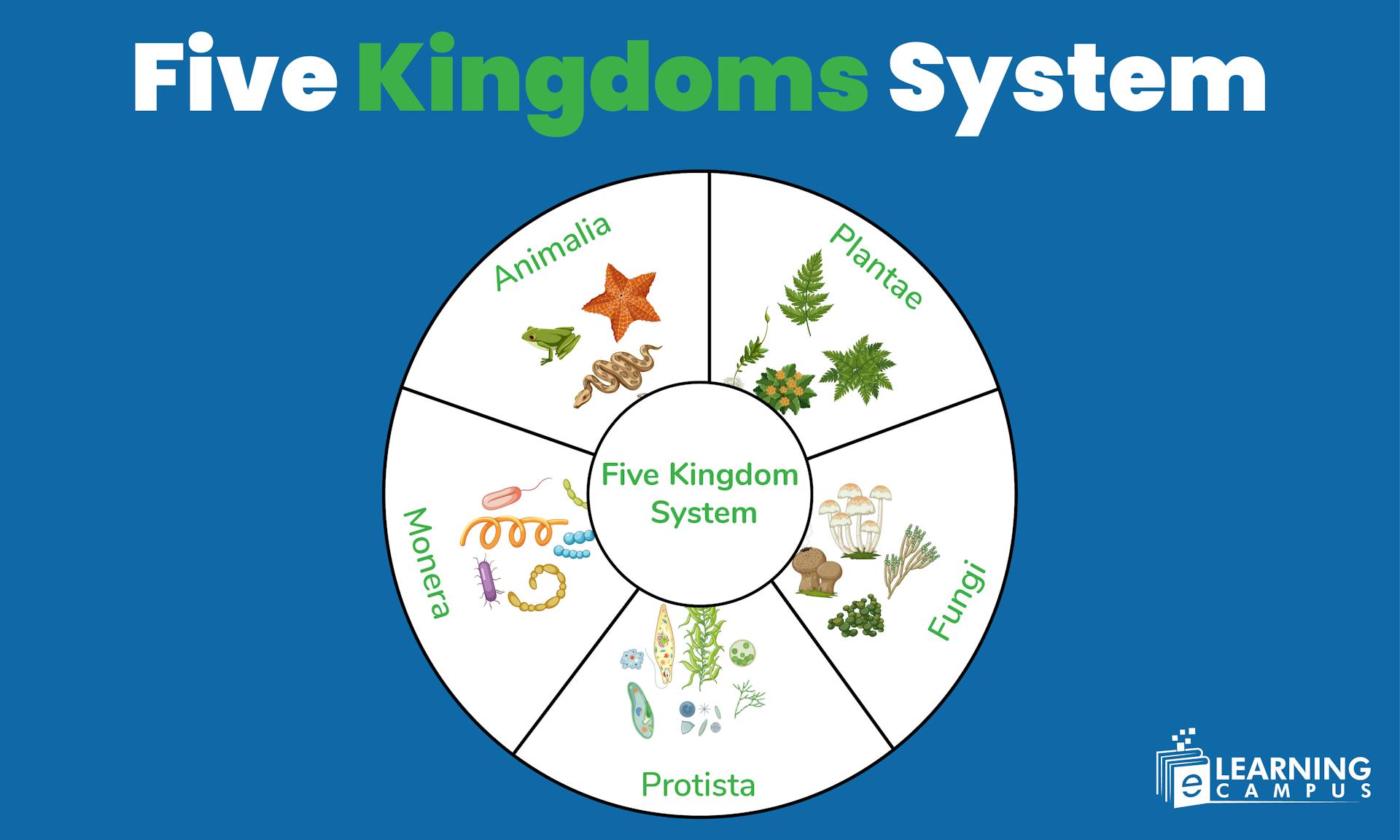
There are millions of living organisms on planet Earth. The study of each organism is a challenging job for researchers and scientists. Therefore, living organisms are classified into five kingdoms system. The proposed five kingdoms of life help study the biodiversity and relationships among the kingdoms.
In this blog, you will learn about the 5 kingdom system, how are organisms classified, and kingdoms of life characteristics.
What is the Five Kingdom System
To differentiate living organisms and make study easy, they are classified into five groups known as the five kingdom system or five kingdoms of life. Organisms are classified based on different characteristics, including cell structure, reproduction, mode of nutrition, thallus organization, and phylogenetic relationships.
The five kingdoms of living organisms are;
- Monera
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Animalia
Background of Classification of Living Organisms
Living organisms have been classified into different kingdoms since ancient times. The five kingdoms of living organisms, or the Whittaker system, is a revolutionary classification.
Two Kingdom System
For centuries, living organisms were divided into two categories, namely, animals and plants. This system was brought to the limelight by Linnaeus in the 18th century.
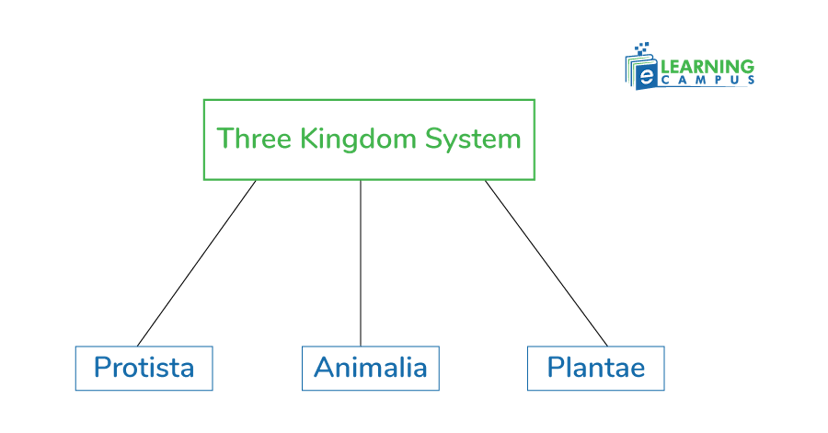
Three Kingdom System
With the discovery of unicellular organisms, Ernst Haeckel in 1866 proposed a third kingdom of life, namely, protists. With this proposition, the two kingdom system evolved into a three kingdom system.
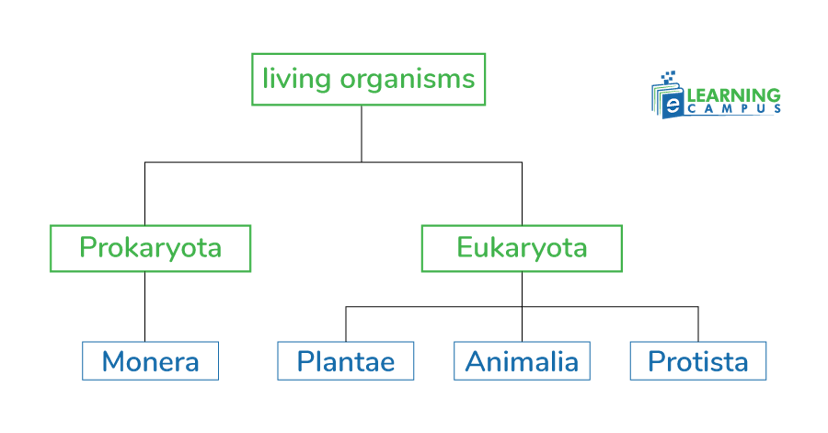
Four Kingdom system
In 1925, Edouard Chatton distinguished living organisms as prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Based on this discovery, Herbert F. Copeland, in 1938, proposed a four kingdom system. He created a new kingdom, Monera, and placed prokaryotes there. At this time, life was categorized into two empires or super kingdoms, i.e, prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Five Kingdom
The 5 kingdoms system was proposed by Robert Whittaker in 1969. included the 5th kingdom, fungi, in the four Kingdom system. This system remained constant for a long time. He diversified the classification based on cell structure, nutrition, and other features.
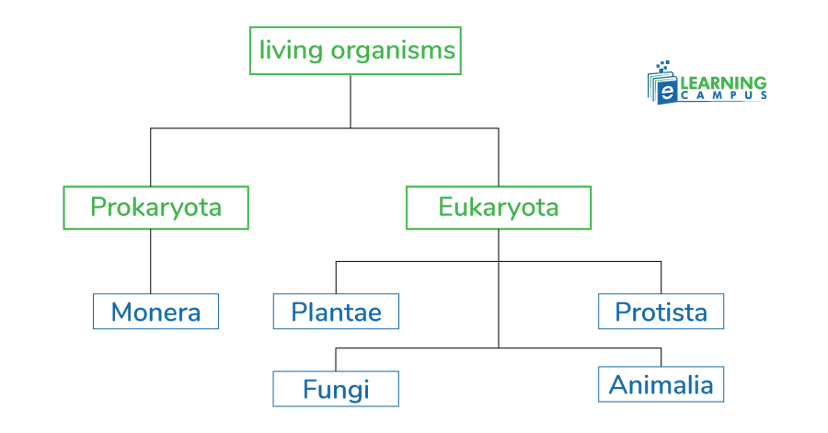
Six Kingdom Classification
Based on the molecular study of prokaryotes, Carl Woese categorized the Prokaryota in Eubacteria and Archaeobacteria. Later, Thomas Cavalier-Smith proposed the six kingdom classification. He created two kingdoms of bacteria– Eubacteria and Archeobacteria. With intense study, living things are grouped into six kingdoms.
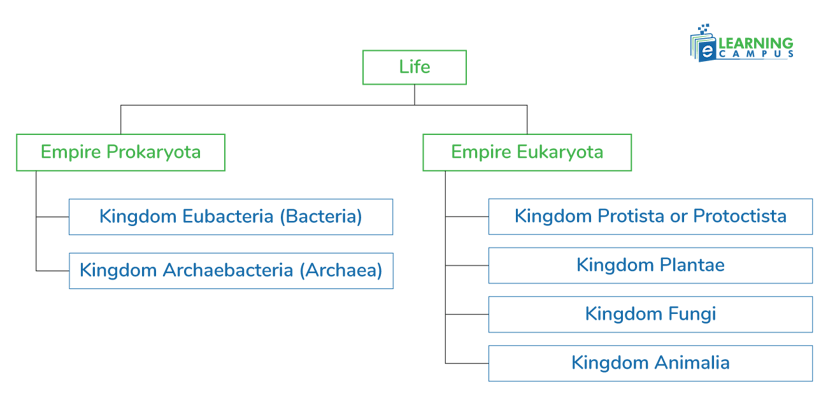
7 Kingdoms of Life
In 2015, Cavalier-Smith and his colleagues revised the 6 kingdoms of living organisms and proposed the 7 kingdoms of life. They proposed two superkingdoms of prokaryota and eukaryota with seven kingdoms. In the 7 kingdoms of living things, prokaryota have two kingdoms, and eukaryota have 5 kingdoms.

Basis of Classification of 5 Kingdoms of Life
Living organisms share various similarities and also have many differences. The differences and similarities involve the structure, functioning, and growth of organisms. The classification of the 5 kingdoms of life is based on the features such as;
Cell Type
An organism can either have prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells. Animals with prokaryotic cells are known as prokaryotes, and those with eukaryotic cells are eukaryotes. The first kingdom, kingdom Monera, has prokaryotes and Animalia, Plantae, fungi, and Protista are the four kingdoms that are eukaryote.
Cell Wall
Some living organisms have a cell wall, while others lack it. The kingdoms Plantae, Monera, and fungi have a cell wall in their cells. Other than these, protists also possess cell walls.
Nuclear Membrane
A cell can have a nuclear membrane or not. All of the kingdoms have nuclear membranes except the organisms in the kingdom Protists.
Cellular Organization
Organisms made up of one cell are known as unicellular, while those with many cells are called multicellular.
Nutrition Mode
Living organisms have two modes of nutrition. Those that make their food are called autotrophs, such as the kingdom Plantae. Those that can’t make their own food and depend on other organisms are known as heterotrophs, such as the kingdoms Animalia and Fungi.
Characteristics of 5 Kingdoms
Whittaker’s 5 kingdoms are based on certain characteristics of living organisms, including mode of nutrition, reproduction, cell structure, phylogenetic relationships, and thallus organization.
This five kingdom classification chart highlights the characteristics of each kingdom.

Modern Classification Hierarchy
An important feature of modern classification systems is that they are the most up-to-date and based on the hierarchy and genetic analysis. Taxonomy, the branch of biology, focuses on the classification of living organisms. Carl Linnaeus, a Swedish Biologist, contributed to the system of classification of living organisms. His hierarchical system is still used for the classification of living organisms. The hierarchical system starts with domain, the largest level, and other levels of classification come under the domain categorically.
The life kingdoms chart below shows the taxonomical hierarchy of classification proposed by Linnaeus.
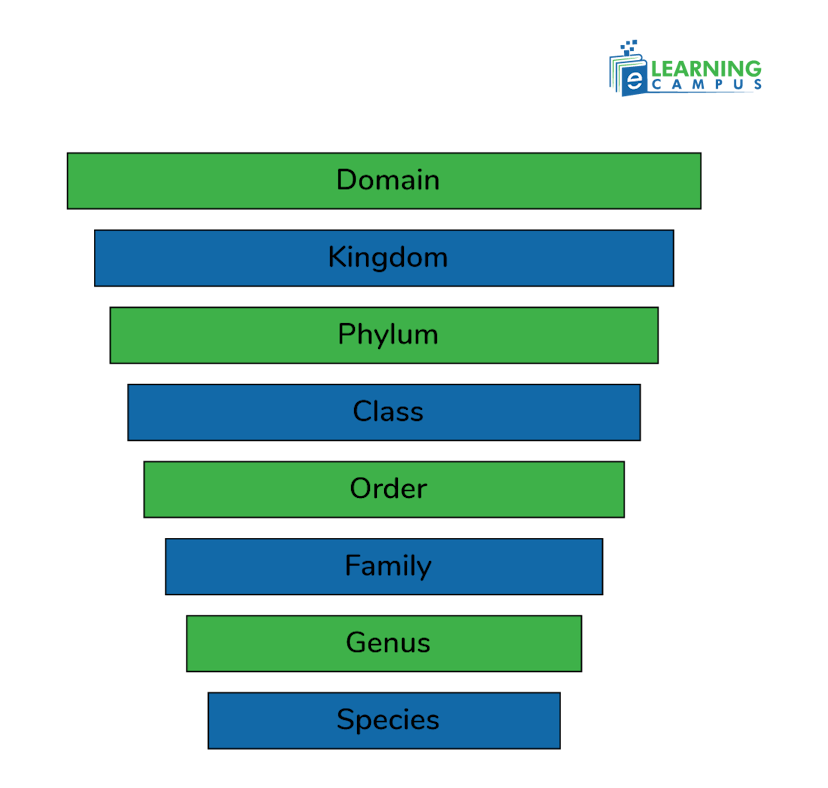
Domain
Domain is the broad category of classification. It includes all living organisms with three empires–Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
Kingdom
A kingdom is a major group within a domain. The five kingdom system includes Animalia, Plantae, Protista, Fungi, and Monera.
Phylum
A phylum is a division within a kingdom. It is based on the body plan or structure of organisms, such as having backbones.
Class
A class includes organisms with general traits, for example, the number of legs in the organism.
Order
The order ranks after the class in the taxonomical hierarchy. Organisms in order have basic common traits such as mammals, carnivors.
Family
The family is classified between genus and order in the taxonomic hierarchy. Organisms in the family are closer to each other. Such as harbors and carnivores.
Genus
Members of the genus are very closely related due to structural similarities. For example, the cat family, Felidae, includes lions, bobcats, tigers, ocelots, lynx, and domestic cats.
Species
Species is the primary unit of taxononical classification and ranks at the last. Same species members have genetic and physical similarities. They also have the same evolutionary history. They interbreed and can give birth to viable offspring.
Conclusion
The five kingdoms system divides organisms into five kingdoms, including Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Before this system, biologists had divided living organisms into different kingdoms. The 5 kingdoms of life is widely accepted and has eradicated the drawbacks of other proposed kingdoms.
Learn Science With Expert Tutor
Are you looking to learn science with expert tutors while sitting at your home? You are a step away. We have professional science tutors to teach your kids at your schedule.