What is An Irrational Number
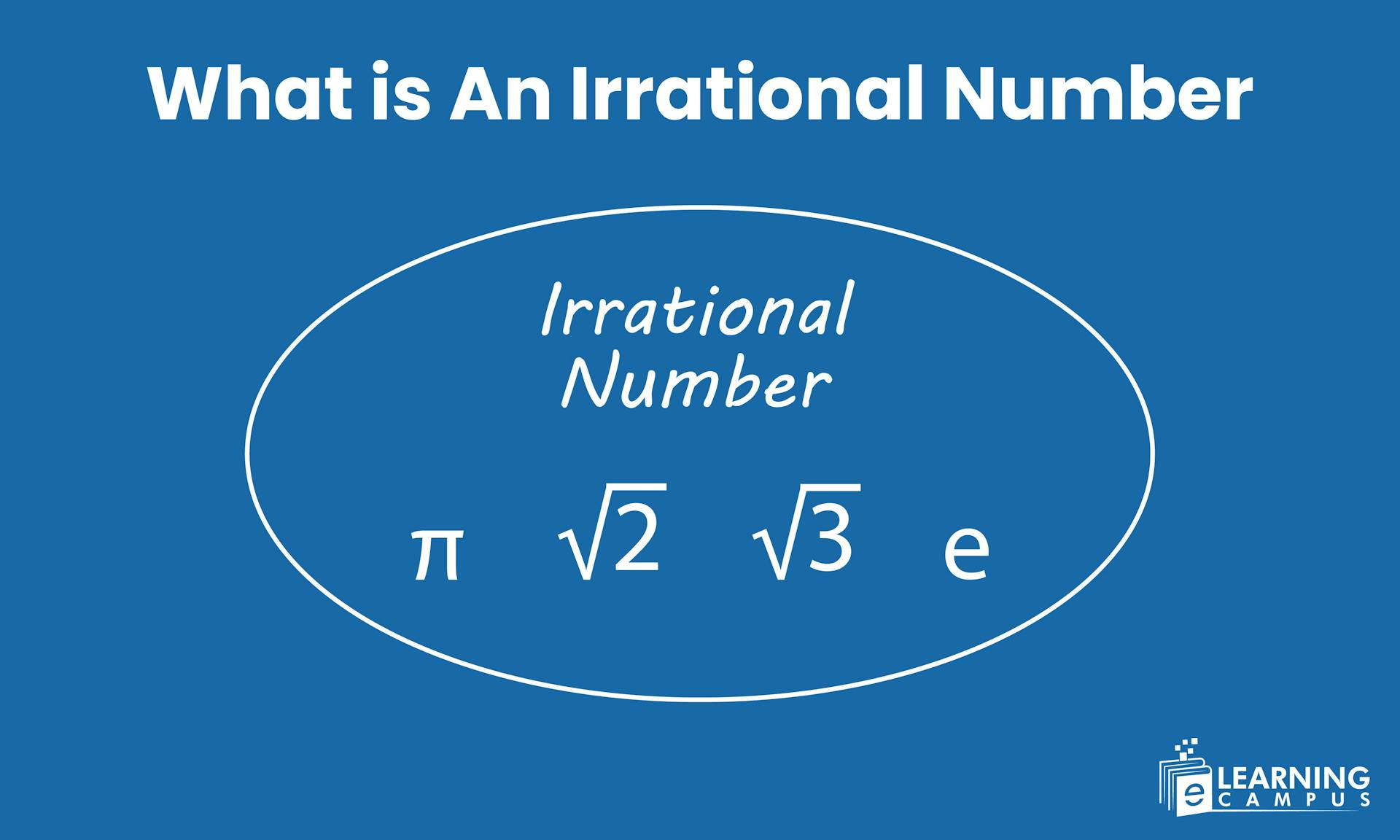
Have you ever seen numbers that never end? These numbers have high importance and applications in mathematics. The numbers like √2 or numbers whose decimal expansion never ends are known as irrational numbers. In simple words, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a ratio of integers and have non-terminating, non-repeating decimals.
In this blog, we provide a complete guide on irrational numbers and rational numbers, their key differences, and learn about some special constants, such as π, square roots, or φ ,
using simple explanations and examples to understand these concepts easily.
What is an Irrational Number?
An irrational number is a real number that cannot be written as a ratio of two integers and has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion.
Irrational number Examples:
- Symbol for irrational numbers
There is no single special symbol used in mathematics for irrational numbers, but we show the set of irrational numbers using R\Q.
- R = set of all real numbers
- Q=Set of numbers excluding rational numbers.
So, the symbolic representation of irrational numbers is: R\Q
Types of Irrational Numbers
There are two types of irrational numbers
- Algebraic Irrational Numbers
Algebraic irrational numbers are any number that is a solution of a polynomial equation with integer coefficients. If an algebraic number cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, it is called an algebraic irrational number.
For example
- Transcendental Numbers
These are numbers that cannot be a solution of any polynomial equation with integer coefficients.
For Example
Characteristics of Irrational Numbers
There are some specifications that make a number irrational, such as being in fraction form, its decimal expansion never ends and never repeats a pattern, always non-terminating, and the square roots of non-perfect squares are features of irrational numbers. Here are the details with examples;
a)Cannot be written as a Fraction
Numbers like √2, √3, and π do not have exact fractional forms. We cannot write them as fractions. These types of numbers are known as irrational numbers.
b) Decimal Goes on Forever
Irrational numbers have infinite decimals, which means they cannot stop.
For example
1.414213562373…….
c) Decimal Never Repeats a pattern
No fixed sequence keeps repeating.
For example:
0.1415926535
π = 3.1415926535…
So, these types of numbers are known as irrational numbers; their decimals go on forever without repeating.
d) Always Non-Terminating
Irrational numbers do not stop, such as 0.5or 3.75. They just continue endlessly.
e) Square Roots of Non-Perfect Squares
The square roots of non-perfect squares are always irrational
For example: √2, √3, √5, √7 are irrational,
but √4 = 2 is rational because 4 is a perfect square.
What are Rational numbers?
A rational number is any number that can be written as a fraction of the form:
a / b
Where:
a and b are integers
b ≠ 0
This means rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction.
Characteristics of Rational Numbers
There are some features of rational numbers, such as: it can be written in fraction form, decimal form terminates after a few decimal values, and it is repetitive.
a)Can be Written as a Fraction form
It can be written as a fraction. Even if a number looks like a decimal or whole number, if it can be written as a fraction, it is rational.
For example
5 = 5 / 1
0.25 = 25 / 100
-8 = -8 / 1
b)Decimal form is Terminating or Repeating
A rational number’s decimal either terminates or repeats a pattern.
For Example
- Terminates(ends)
0.5,3.75, 9.2
These stops after a few decimal places, so they are known as rational numbers
- On the other hand, it repeats a pattern
For example
0.33333…..(3 repeats )
0.121212…. (12 repeats )
5.677777……(7 repeats )
So, repeating decimals are also known as rational numbers.
Is Pi irrational?
Yes,π\(Pi) is rational because its decimal never ends and remains continuous without repeating, and cannot be written as a fraction.
- Pi represents the ratio of the circle circumference and its diameter. The value of is 3.14592653589793…There are the following reasons that pi is irrational;
Cannot be written as a Fraction.
A rational number can be written as a fraction, but pi cannot be written as a fraction; even 22/7 is only an approximation, not the exact value.
Pi’s Decimal Never Ends
The decimal expansion of continues forever, e.g, 3.1415926553589799323…..There is no final digit, no endings, which makes them irrational.
Pi’s decimal never repeats a pattern
A rational number either ends or repeats after some decimal place, or repeats, such as 0.3333, etc.
But never ends and goes on infinitely.
Proven by a Mathematician
In 1768, the mathematician Johann Lambert proved that π is irrational. He showed that it cannot satisfy any equation of the form:
ax² + bx + c = 0
where a, b, and c are whole numbers.
Pi is also a Transcendental number
This means it is even more special:
- It is irrational
- It cannot be a solution of any polynomial equation
- It is beyond algebra
Note: But Pi’s irrationality matters because it can be used in geometry, trigonometry, physics, engineering, architecture, and calculus, etc. Its irrational nature helps create accurate formulas for circles, wave motion, and more.
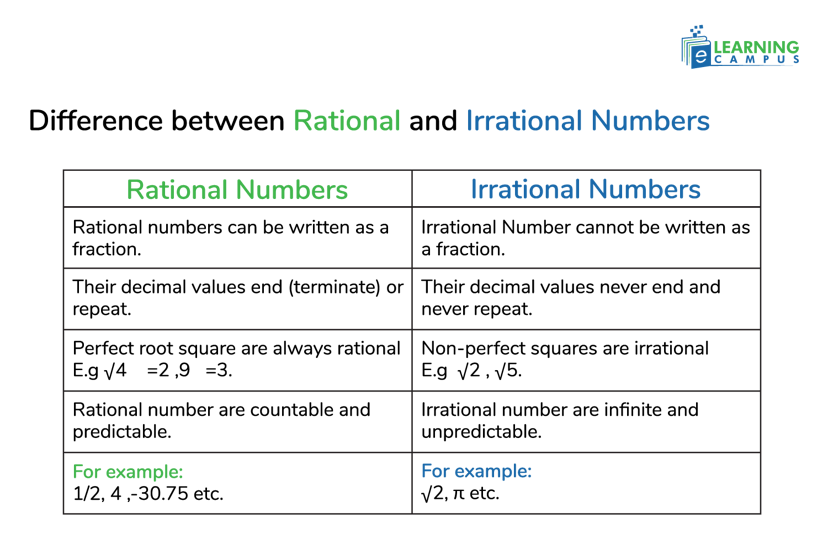
Difference between Rational and Irrational Numbers
In mathematics, numbers are divided into two important groups: rational and irrational numbers. Understanding the difference between them helps us make sense of everything from simple fractions to complex calculations.
Here’s the difference ;
Is 0 irrational?
No, 0 is not an irrational number.
Irrational numbers cannot be written as a fraction, but zero can be written as a fraction. So, it does not fulfil the requirements of an irrational number; that's why 0 is a rational number.
For example
It can be written as a fraction, e.g 0/1,0/2, etc.
How to prove a number is irrational
To prove a number is irrational if it can be written as a fraction p/q.
Where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. You can also prove this from another famous method.
Proof by Contradiction
You assume the number is rational, then show that assumption leads to a contradiction.
For Example
√2 is irrational.
Assume √2 is rational. So we can write it as
√2 = p / q …eq (1)
where p and q have no common factors.
Squaring both sides, equation (1) becomes:
2 = p² / q²
So, p² = 2q
This means p² is even, so p is even.
Let p = 2k
Substitute back, and you get q is also even.
But if both p and q are even, they have a common factor (2). This contradicts the assumption.
Therefore, √2 is irrational.
What is the Golden Ratio (φ)?
The golden ratio is a special number that appears in mathematics. It is denoted by φ, and also called Phi, and it is an irrational number due to a non-terminating and non-repeating decimal expansion.
Its value is equal to:
φ = (1 + √5) / 2 ≈ 1.618033
Why is phi (φ) irrational?
Phi (φ) cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, so it is irrational.
Its decimal expansion is non-terminating and non-repeating.
So, the golden ratio is an irrational number with infinite non-repeating decimals, and it is a simple algebraic equation.
How to add Irrational numbers
You can simply add the irrational numbers by simply a formula.
Formula = a + b
Case 1: The sum of two irrational numbers remains irrational
√2 + √3
It cannot be simplified into a fraction, so it is irrational.
Case 2: Sum of two irrationals becomes rational
√2 + (-√2) = 0
Here the sum can be cancelled out, so it becomes rational.
Case 3: Adding rational and irrational
3 + √2 ≈ 3 + 1.414 = 4.414
Now this is non-terminating, non-repeating, so their output becomes irrational.
How to Multiply Irrational Numbers
You can simply multiply the irrational numbers by a formula.
Formula = a × b
Case 1: The product of two irrationals remains irrational
√2 × √3 = √6
So, √6 cannot be expressed as a fraction, so it is irrational.
Case 2: Product of two irrational numbers becomes rational
√2 × √2 = 2
Here, the product is rational.
Conclusions
Irrational numbers are the numbers that cannot be represented as a fraction and have non-terminating, non-repeating decimals, such √2, φ. Their presence in geometry, algebra, calculus, and real-world measurements shows how essential they are for accurate calculations and deeper mathematical understanding. Our blog will help you in recognising irrational numbers that strengthen your basic math concepts and problem-solving skills.
Learn math online with expert Tutors
Want to deepen your understanding of numbers and more math concepts? Don't worry, our expert online math tutors can help you. Our expert online tutors explain every concept in simple and clear steps, whether it's homework support, improving your basics or exam preparation. Get benefits from our online tutoring service and start learning math now.
