Wavelength to Frequency Conversion and Relationship
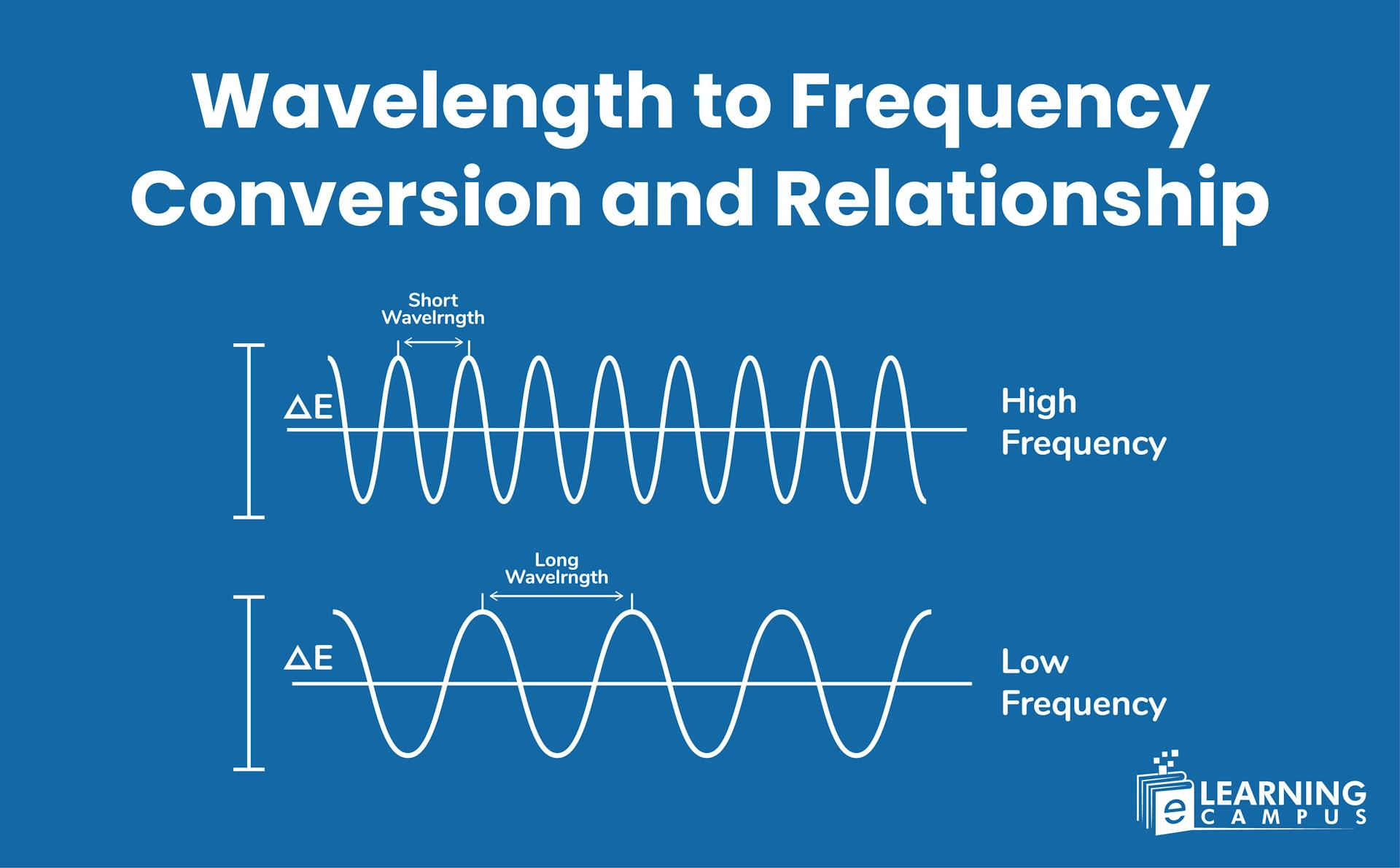
Wavelength is the distance from one crest or trough to another. Frequency is the number of waves that pass a given point per second. The relationship between wavelength and frequency is inversely proportional. It means that as wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and vice versa. Wavelength can be converted to frequency by dividing the speed of light by the wavelength.
Wave Length
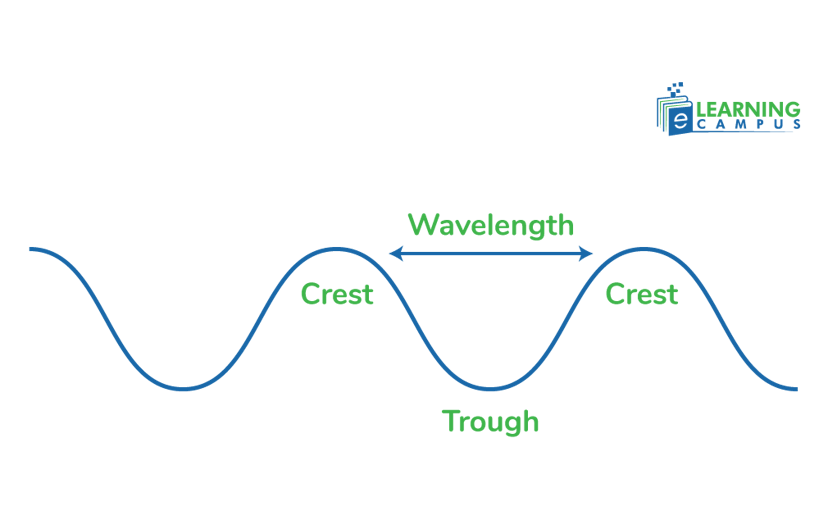
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive corresponding points on a wave. It is the distance from one crest of a wave to another or from one trough to another in a transverse wave. It represents the spatial period of a wave. The wavelength indicates how quickly the shape of the wave repeats. It is denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ).
Wavelength Formula
The wavelength formula explains the relationship between wavelength to frequency, and speed. Mathematically, the formula is written as;
Where,
- where 'v' is the velocity or speed of the wavelength.
- 'f' is the frequency of the wave.
The equation shows that a wave with a higher speed will have a longer wavelength, and a wave with a higher frequency will have a shorter wavelength.
The unit of measurement of wavelength is length, usually measured in nanometers (nm), meters (m), or centimeters (cm).
Frequency
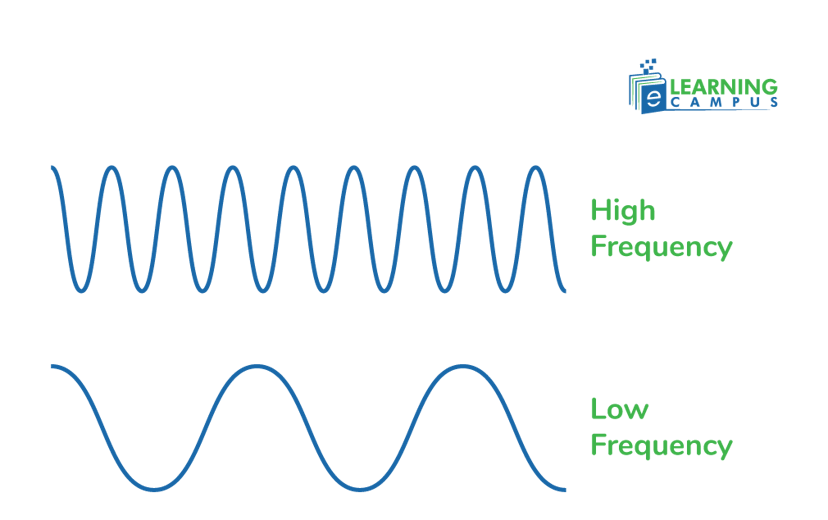
Frequency is the repetition of a phenomenon in a given period. Wave frequency refers to the number of wave cycles that pass a fixed point in a given amount of time, typically per second.
Frequency Formula
The frequency formula helps us find the frequency of a wave. The general formula to calculate the wave frequency is given as;
Where 'f' is frequency and 'T' is the time taken for one cycle to complete. This formula is used when the time it takes for a single cycle is known.
When wave speed (v) and the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs (wavelength, λ) are given, then this formula will be used to find the frequency of the wave.
The unit of measurement of frequency is ‘Hertz’, denoted by ‘Hz’.
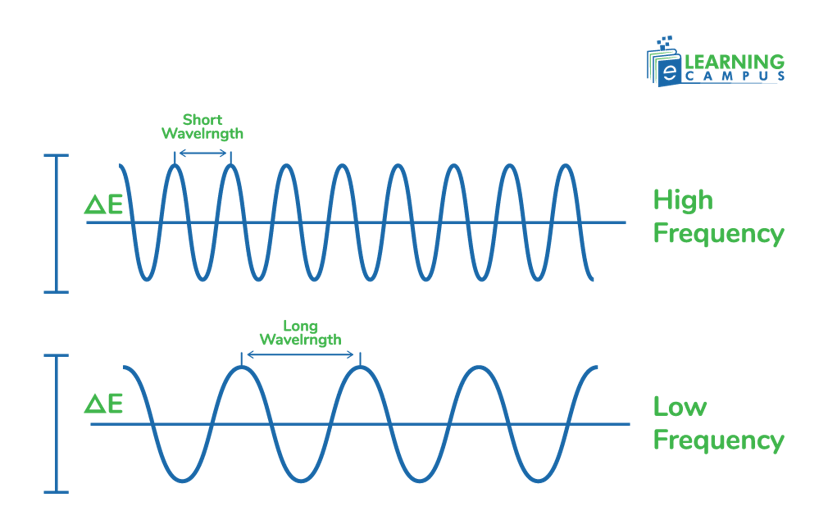
Relation between Frequency and Wavelength
There is an inversely proportional relationship between frequency and wavelength. This means that when the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and when the wavelength increases, its frequency decreases.
The relationship means that for a constant speed, such as the speed of light in a vacuum if we increase the frequency, we must decrease the wavelength to maintain the same speed.
This relationship is expressed by the formula as;
Where,
- 'c' is the speed of light
- 'f' is the frequency.
- 'λ' is the wavelength.
Converting Wavelength to Frequency
Wavelength can be converted to frequency by dividing the speed of light by the wavelength. The formula used for this conversion is,
The speed of light (c) is 3.00 x 108 meters per second. Let’s understand it with an example.
Blue light has a wavelength of about 500nm. Find the frequency.
First, convert nm to m. So, 500nm is equal to
Putting the values in the formula.
So, the frequency of the blue light with a wavelength of 500 nm is
Converting Frequency to Wavelength
Frequency is converted to wavelength by dividing the speed of the wave by its frequency. For electromagnetic waves such as light in a vacuum, this is done by dividing the speed of light by the frequency in Hertz.
The formula for frequency to wavelength conversion is given as;
Where,
- ‘λ ’ Lambda is the wavelength.
- ‘C’ is the speed of light
- ‘F’ is the frequency of the wave.
Let's understand it with the help of an example.
The frequency of a wave is 110 MHz. Find the wavelength.
To find the wavelength, we will use the formula.
Convert 110 MHz to Hz, which is equal to 1.1×108
The speed of light is 3.00 x 108
Put the values in the formula
So, the length of the wave with a frequency of 110 MHz is 2.73m.
Conclusion
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional properties of a wave, which means that as one increases, the other decreases. Frequency and wavelength are interconvertible. If one value is given, we can find the other value.
Learn Physics Online With Us
Are you struggling with Physics and want to learn with an expert tutor? Hold on. We have professional physics tutors to make the subject easy for you. You will get targeted preparation for your exams.