Phosphate Functional Group
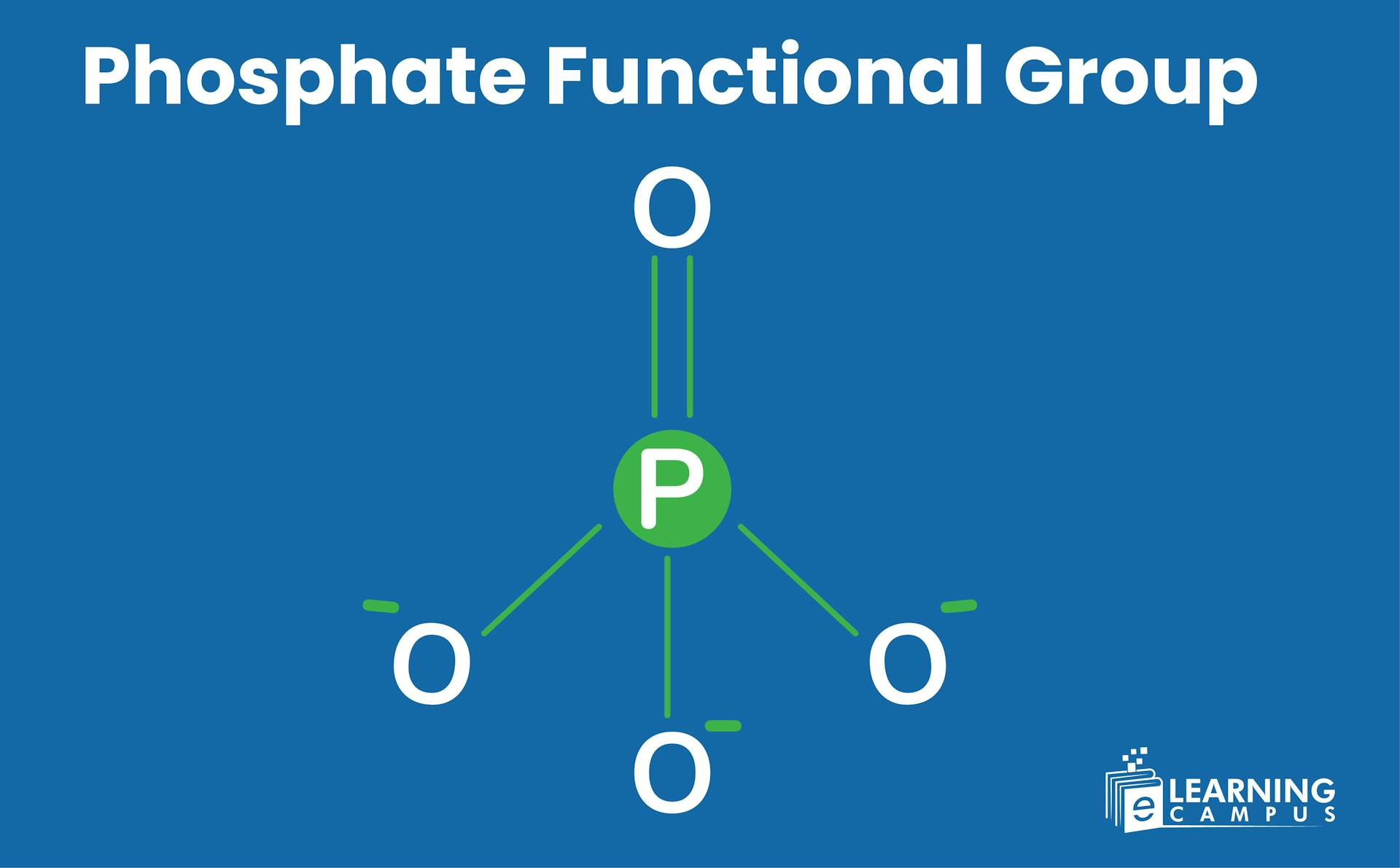
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms within a molecule that exhibits similar chemical behavior in various compounds. A phosphate functional group consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms. One of those oxygen atoms forms a double bond, and the other three form single bonds.
It plays an important role in various biological and chemical processes, including those involving DNA, RNA, ATP, and cellular structural components.
Structure of Phosphate Group
The structure of the phosphate functional group represents the arrangement of its constituent atoms within a molecule. The basic structure of the phosphate group is a tetrahedral shape. Four oxygen atoms are bonded to the central phosphorus atom.
One oxygen atom forms a double bond (P=O) with the phosphorus atom. The remaining three oxygen atoms form a single bond with the phosphorus atom. Due to three single bonds, it is represented by negatively charged oxygen atoms (PO₄³⁻). The negative charge is important for its interactions with other molecules.
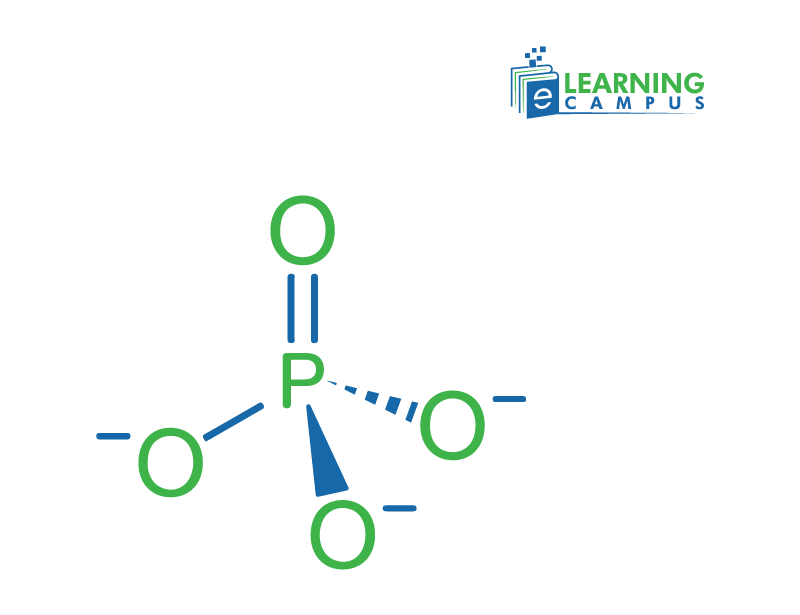
Phosphate Group Formula
A chemical formula is a symbolic representation of the chemical composition of a molecule or compound. The chemical formula for the phosphate functional group is PO₄³⁻. This formula shows that four oxygen atoms ‘o’ make a bond with the phosphate atom ‘p’.
Properties of the Phosphate Group
The phosphate group has high importance in chemical and biological science. This molecule exhibits some unique physical and chemical properties
Physical Properties
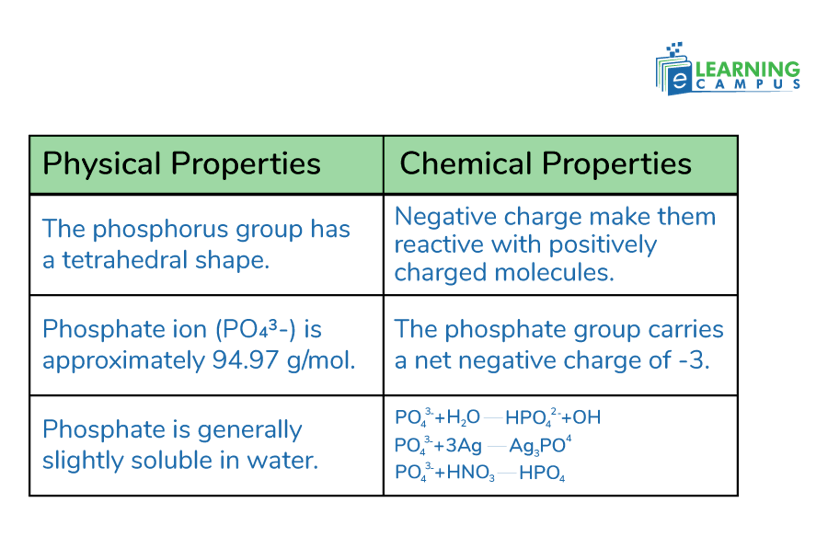
Physical properties of a molecule describe characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the chemical composition of the molecule. The physical properties of the phosphate group are as follows;
Structure
The phosphorus group has a tetrahedral shape. It features a central phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms.
Molecular Weight
The molecular weight of the phosphate ion (PO₄³⁻) is approximately 94.97 g/mol.
Solubility
Phosphate is generally slightly soluble in water. While the phosphate ion itself has limited solubility. Many phosphate salts (like sodium, potassium, etc.) are soluble in water.
Chemical Properties
A chemical property of a molecule describes how it behaves during a chemical reaction, specifically how its molecular structure changes. The chemical properties of the functional group of phosphate are given here.
Reactivity
Phosphate groups carry a negative charge, making them reactive with positively charged molecules.
Charge
The phosphate group carries a net negative charge of -3.
Reactions with Other Elements
The phosphorus functional group reacts with other elements to produce a new product.
- Its reaction with water produces hydrogen phosphate and free hydroxide ions.
PO43-+H2O→HPO42-+OH-
- It reacts with silver to give silver phosphate
PO43-+3Ag→Ag3PO4
- In reaction with nitric acid, phosphate gives nitrate and hydrogen phosphate.
PO43-+HNO3→NO3+HPO4
Functions of the Phosphate Functional Group
The phosphate groups play an important role in living organisms. They are vital components in structural support, energy transfer, and cellular signaling. Here are the functions of phosphate groups in detail.
Role in Nucleotides
Nucleotides are the building blocks of genetic material such as DNA. The phosphate group in a nucleotide forms the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA and RNA that connects nucleotides together to create long chains. The negative charge on phosphate stabilizes the double helix structure of DNA and facilitates interactions with other molecules, like proteins.
Energy Transfer
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a molecule that serves as the primary energy carrier for cellular processes. It is composed of denine, ribose, and a chain of three phosphate groups.
The phosphate groups in ATP store energy in their chemical bonds. The bonds between the phosphate groups are high-energy bonds. When these bonds are broken, they release energy that the cell can use for various cellular processes.
Protein Activation
Phosphate has a critical role in protein activation in the cell. Phosphorylation is a biochemical process in which a phosphate group is added to a molecule, often a protein, to activate it. Dephosphorylation is the removal of a phosphate group from a protein, which makes it inactive.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are the basic components of cell membranes. They are composed of a phosphate group attached to a polar head group. The phosphate group is also linked to other molecules, such as choline, ethanolamine, serine, or inositol, creating a diverse range of phospholipid structures.
Act as Buffer
Phosphate acts as a buffer by resisting changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added to a solution. Phosphate buffers are important in maintaining pH levels within cells and the kidneys. In the kidneys, it helps regulate the pH of urine by neutralizing excess hydrogen ions.
Conclusion
A phosphate functional group consists of a phosphorus atom that makes bonds with four oxygen atoms. One phosphorus-oxygen bond is double and three are single bonds. It plays a vital role in various biological molecules and processes, including DNA, RNA, and energy transfer molecules like ATP.
Hire Online Science Tutor
Are you struggling with science? Don’t worry. We can help you learn science subjects from your own home. We have expert tutors ready to make the subject easier for you. You will get targeted preparations for your exam and tests.