PEMDAS and Its Rule
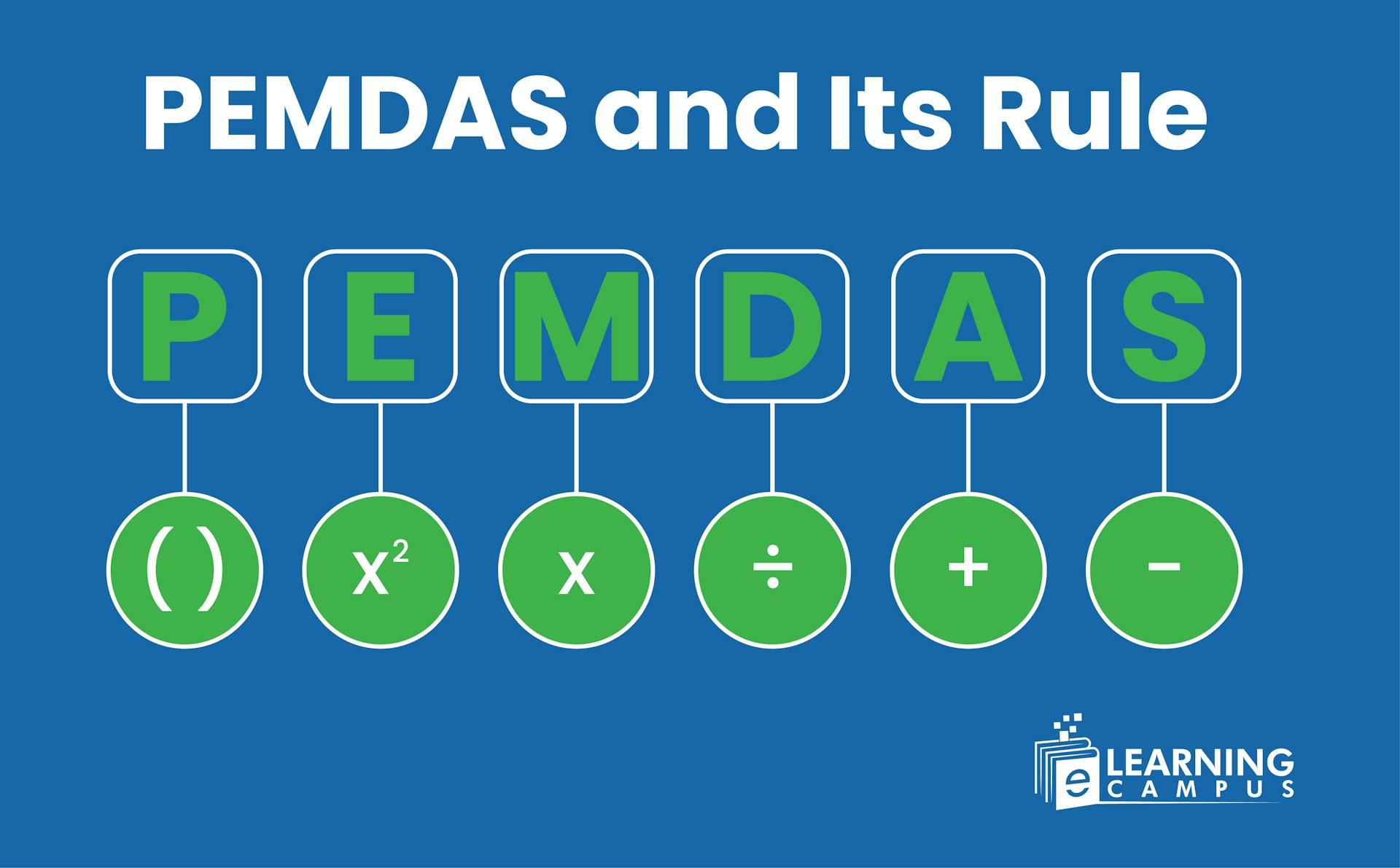
PEMDAS is the order of operations mnemonic that helps to remember the order while applying operations in mathematics. It is the acronym for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division and Addition, and Subtraction. Understanding PEMDAS and its rules is crucial for doing accurate mathematical calculations.
What is PEMDAS
The mathematical calculations are based on arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication. While carrying out the operations, certain rules are applied, known as the PEMDAS rule. PEMDAS is an acronym for order of math operations. It’s full for is given below.
- P stands for Parentheses [{()}]
- E stands for Exponents (Powers or Roots)
- MD stands for Multiplication and Division (from left to right) (× and ÷)
- AS stands for Addition and Subtraction (from left to right) (+ and -)
PEMDAS Rule
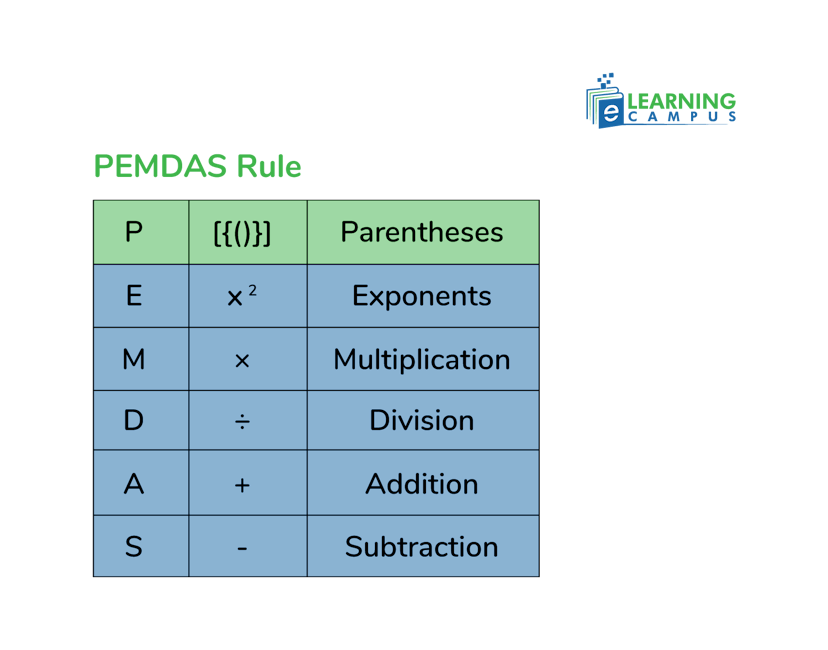
The PEMDAS rule deals with the order of operations while doing Mathematical calculations. This rule states that ‘if any mathematical expression contains all arithmetic operations, including parentheses and exponents, then the operation will start with parentheses followed by exponents, multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction.
Let’s look deep into it.
If there is a complex math expression that contains parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction, then the order of operations follows as;
- Parentheses (P): Solve the parentheses first. It means the operations that are present in the bracket, i.e, small brackets( ), curly brackets{ }, or big brackets[ ], will be solved first. If there are three brackets, then begin operation from the innermost bracket.
- Exponents (E): The calculations that include exponents should be solved first, but after the parentheses. The exponential expressions are represented as a square root or a power, such
- Multiplication or Division(MD): The multiplication and division will be solved from left to right. It means that whichever operation comes first in the equation will be solved first. For example, in an equation, division appears first then it will be calculated with priority. Also, in an equation where multiplication comes first will be calculated earlier.
- Addition and Subtraction (AS): Addition and subtraction will be calculated from left to right. Whichever comes first will be solved accordingly.
Solving Problems Involving PEMDAS
It is easy to solve PEMDAS Problems if we understand the rule. We will learn to solve the problems that involve the PEMDAS rule. Let’s look at the PEMDAS examples with answers.
Example
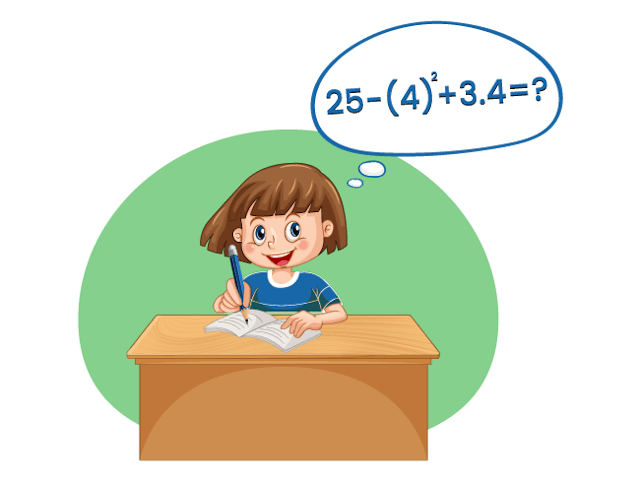
Solve
To solve this expression, we will follow the rule of PEMDAS.
First, we will solve the parentheses. In the given expression
involves parentheses. So, we will solve it first. So,
In the second step, we will solve expression that involve exponent or power.
contains an exponent, we will solve it first.
Then, we will look for multiplication and division. Whichever operation comes first will be solved first. In this expression, division comes first, so we will divide the expression.
Multiplication also appears in the expression, therefore, we will solve it after division.
Next, we will look for addition and subtraction. The operation that appears first will be solved first. In this expression, plus + comes first. Therefore, we will add the numbers first.
At the end, we are left only with subtraction, as it comes after plus in the expression.
So, we solved the order of operations math problem using the PEMDAS rule. Now you can solve any type of math problem using this method.
Order of Operations Mnemonic
The order of operations is a set of rules that tells how and which operations should be performed first. There are several order of operations mnemonics that help to solve mathematical expressions. One of the mnemonics is ‘Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally’. In the order of operations my dear Aunt Sally, each word is an acronym for different operations. Let’s look into it in detail.
- P of Please represents parentheses.
- E of excuse is used to remember the exponent.
- M of My shows multiplication.
- D of Dear represents the division.
- A of Aunty is used for addition.
- S of Sally is used to remember subtraction.
So, please excuse my dear aunt Sally is an example of math mnemonics used to remember the order of operations while calculating mathematical expressions and equations.
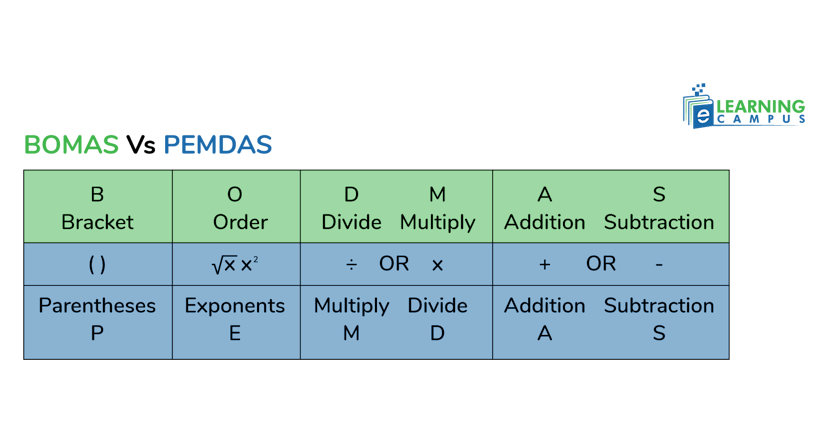
Bodmas vs Pemdas
PEMDAS and BODMAS are different acronyms for the same order of operations in mathematics, used to simplify expressions with multiple operations. BODMAS stands for Brackets, Order (or powers), Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction. PEMDAS stands for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction. While they use slightly different terminology (Brackets/Parentheses, Orders/Exponents), they both represent the same rules for the order in which operations should be performed.
Conclusion
PEMDAS stands for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction. It is a mnemonic device for remembering the order of operations in mathematical expressions.
Learn Math with Live Tutor
Are you struggling with Math and want to learn with expert live tutors? You are at the right place. We have professional online math tutors to address all your math problems. You will get personalized instructions on topics.