Parts of Speech| Definition, Types and Examples

We talk every day. We speak to friends, family members, and strangers regularly. Have you ever thought about what role do Parts of Speech play in our daily communication orally or verbally?
The parts of speech are crucial for speaking and learning the proper English language. There are 8 parts of speech including nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. However, some dictionaries mention articles as the parts of speech that make it 9.
In this blog, you will learn what the Parts of Speech are and the 9 parts of speech with definition and examples in detail. Let’s learn them one by one.
Parts of Speech Chart
Students usually forget the definitions of the parts of speech and become confused about them. We will provide you with a chart on parts of speech to help you get a clear idea about them. You will easily understand and remember with the help of the parts of speech chart.
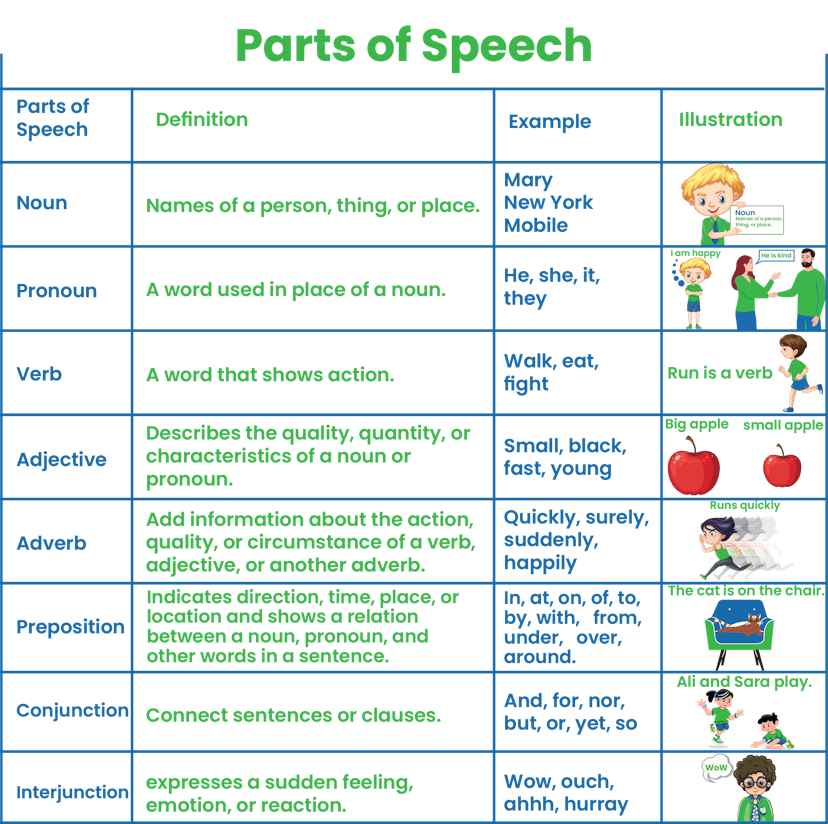
Noun
A noun is a word used to describe a person, thing, place, or any idea or concept. Everything in the universe is a noun.
For example,
- Paul Smith is a person.
- A laptop is a thing.
- Columbia is a place.
- Democracy is an idea or concept.
- In the above examples, Paul Smith, Laptop, Columbia, and Democracy are nouns.
Types of Noun
Nouns are divided into different categories based on their characteristics and use in sentences. There are 8 types of nouns. Let’s learn the types of nouns in English with examples.
Proper Noun
A proper noun describes a specific person, place, or thing. For example,
Donald Trump and Nelson Mandela are names of specific people.
New York and Bombay are the names of specific places.
Dell laptops, bananas, and roses are the names of specific things.
So, the names of specific persons, places, and things are the proper nouns.
Common Noun
A common noun describes the general perspective of people, places, and things.
For example,
Boy, women, and baby refer to general people, not a specific person.
Country, garden, and school describe general places.
Car, book, and tree describe general things, not a specific one.
Countable Noun
Countable nouns refer to names of things that can be counted easily. Such as people, cups, apples, and countries.
Uncountable Noun
The uncountable nouns are the names of things that cannot be counted. For example, water, milk, information, rice, and soil.
Concrete Noun
The concrete noun refers to the name of things that can be seen and touched, such as mobile, elephant, and tree.
Abstract Noun
Abstract noun refers to emotions, feelings, or ideas that can only be felt but not seen or touched. For example, love, sadness, happiness, justice, etc.
Collective Noun
A collective noun refers to a group of people or things that are considered as a single unit or entity. For example, the army, students, herd, flock, etc.
Pronoun
A pronoun is a word that is used instead of a noun. It is written in place of a previously used noun in a sentence. For example, he, she, it, they.
Types of Pronoun
Personal Pronoun
A word that is used in place of a person’s name is known as a personal pronoun. It helps create fluency in sentences by avoiding access use of names. For example, he, she, it, they, we, I, and me are some examples of personal pronouns.
Demonstrative Pronoun
A demonstrative pronoun points to specific things or people that have been mentioned in a sentence or conversation (antecedent ). For example, this, that, these, and those.
Interrogative Pronoun
Interrogative pronouns introduce questions related to any person or thing. Such as who, whose, whom, which, etc.
Verb
Verbs are words that show action, event, or state of being. A verb in a sentence highlights the action of the subject. For example, Sara is reading. In this sentence, reading is a verb and shows Sara’s action.
The examples of verbs are walk, read, sleep, fight, etc.
Types of Verbs
Regular Verb
Regular Verbs are those whose second form and third forms are formed by adding ‘d’ or ‘ed’ at the end of the verb. Such as check, follow, and drop.
Irregular Verb
Irregular verbs are those whose second form and third forms can’t be formed by adding ‘d’ or ‘ed’ at the end of the verb. For example, see, cut, read, etc.
Adjective
An adjective describes the quality, quantity, or state of a noun or pronoun. It modifies the quality of nouns. For example, a tall boy, a red car, pleasant weather, a huge house.
In these examples, tall, red, pleasant, and huge are adjectives that describe the quality of boy, car, weather, and house respectively.
- The comparative adjective compares two or more than two things. Such as Smith runs faster than Archer.
- The superlative adjective describes the noun as being the most or least in the character.
For example, Stuart is the tallest boy in class, the leopard is the fastest animal, and Anaya is the laziest girl.
In these sentences, tallest, fastest, and laziest are superlative adjectives.
Adverb
Adverbs modify a verb, sentence, or adjective. It is formed when the suffix -ly is placed at the end of the adjective. Such as the adjective ‘quick’ will become ‘quickly’ by adding -ly at the end.
The examples of adverbs are slowly, extremely, incredibly, magically, etc.
Preposition
Prepositions are specific words that appear before a noun or pronoun in a sentence and express the relation with other words or elements in a clause.
Let’s look at these sentences to understand the preposition with examples.
The book is on the table.
They will be arriving at 7:00 p.m.
Ruby went to college.
In the above sentences, on, at, and to, are examples of prepositions.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions connect the different parts of sentences, including words, phrases, and clauses. Let’s look at examples,
Sara likes reading and playing.
Mary is ill. So, she can’t attend class.
You can either take the coffee or order a burger.
In the above examples, the words and, so, either, and or are some of the examples of conjunction.
Interjections
The interjection shows sudden feeling, enjoyment, greeting, or a command. Interjections are an important part of English writing. However, they can be excluded from the sentence in a way that does not change the meaning of the sentence.
Example,
Hurrah! We won the match.
Wow! This is incredible.
Ahhh! She is no more.
Find Online English Tutor
Are you struggling with reading and speaking English? We got you. We have expert English tutors to teach you English in a professional way with a schedule that fits your routine.
