Eukaryotic Cells
About 2 billion years ago, life on Earth was dominated by bacteria and archaea, which were composed of prokaryotic cells. The evolution of Eukaryotic cells drastically changed life. They are more complex than prokaryotic cells and are the building blocks of different species of multicellular organisms. The eukaryotic cells refer to the cells that make up animals, plants, fungi, and protozoa.
What is Eukaryotic Cell
The word eukaryote is derived from the Greek language. In which, ‘eu’ means ‘true’ or ‘good’ and ‘karyon’ means ‘kernel or seed’. So, the cell with a good seed or kernel is eukaryotic.
In biological terms, a eukaryotic cell is a cell that possesses a clear nucleus, a nuclear membrane, and different cytoplasmic organelles specialized for specific functions.
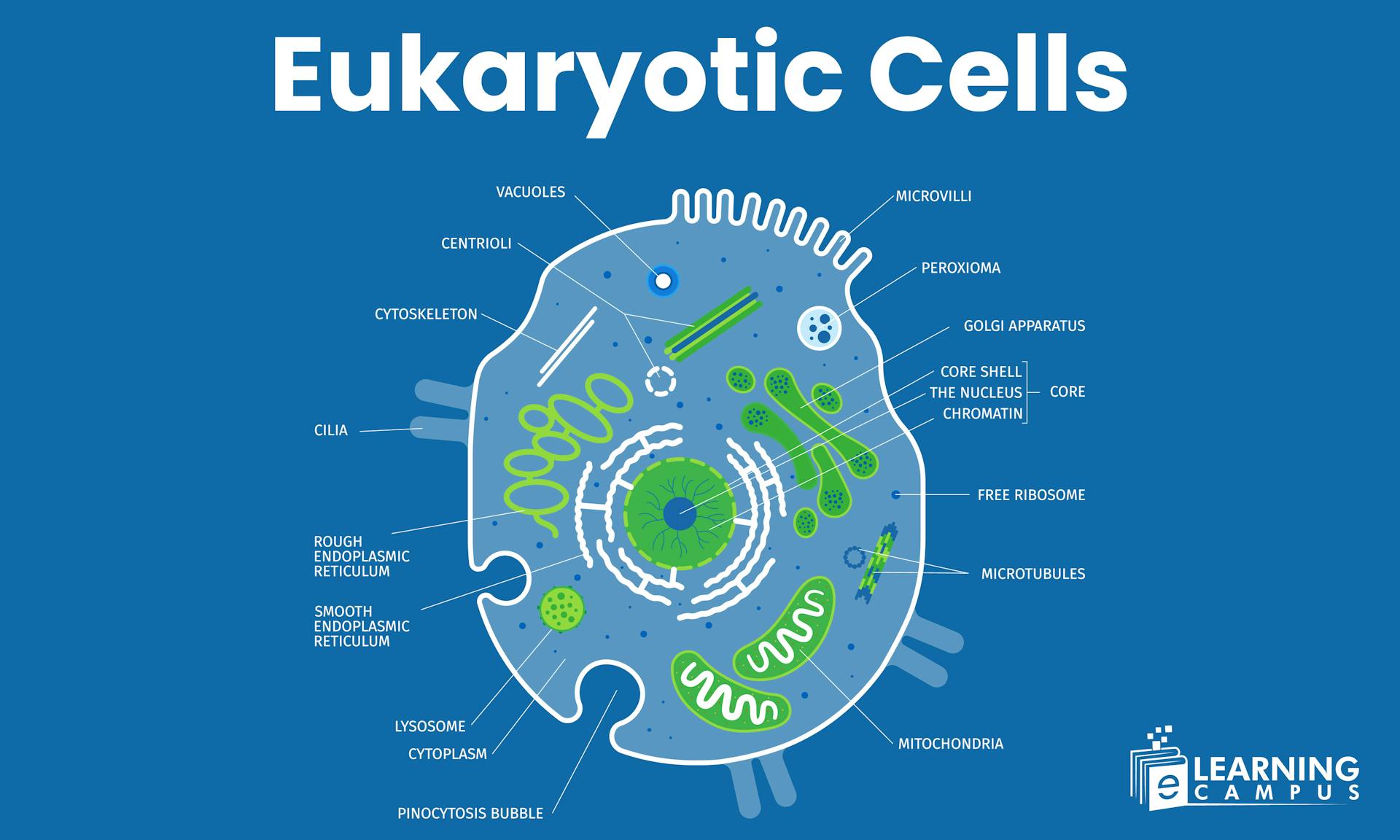
Eukaryotic Cells Labeled Diagram
A eukaryotic cell has a complex mechanism. It possesses various organelles that have specific functions within the cell. The eukaryotic cells labeled diagram, showing different organelles, helps you understand the cell structure and function of different organelles.
Structure of Eukaryotic Cells
From the complex mechanisms of humans to the irregular shape of plants, eukaryotic cells are the foundation for these multicellular organisms. These cells have different organelles, which make them a complex structure.
Membrane Bound Organelles
A eukaryotic cell contains many compartmentalized organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and vacuole. These organelles have specialized functions and play an important role in the life of organisms, including energy production, protein synthesis, and transport.
Nucleus
Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear envelope. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is found in the nucleus. It is, therefore, an essential site for gene expression, replication, and cellular division. The nuclear envelope contains pores that regulate the movement of substances in and out of the nucleus.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles and are the powerhouse of energy production. It is believed that eukaryotic cells acquired mitochondria and chloroplasts by a process called endosymbiosis. Mitochondria have their own DNA, having structural similarities to that of bacterial DNA.
Cytoplasm
The eukaryotic cells have cytoplasm, a jelly-like substance within the cell that surrounds the organelles. It is a thick solution made up of water, protein, and salts. It consists of cytosol, cytoskeleton, and organelles.
Reproduction
The life cycle of a eukaryotic cell involves sexual and asexual reproduction. Eukaryotes can reproduce sexually through meiosis and gamete fusion and asexually through mitosis. In mitosis, cell division occurs, while in meiosis, reproduction occurs through the production of eggs and sperm.
Size of Eukaryotic Cell
The eukaryotic cells are bigger than prokaryotic cells. The size of Eukaryotic Cell typically ranges from 10 to 100 micrometers (µm) in diameter. While the prokaryotic cell ranges from 0.1 to 5.0 µm in diameter.
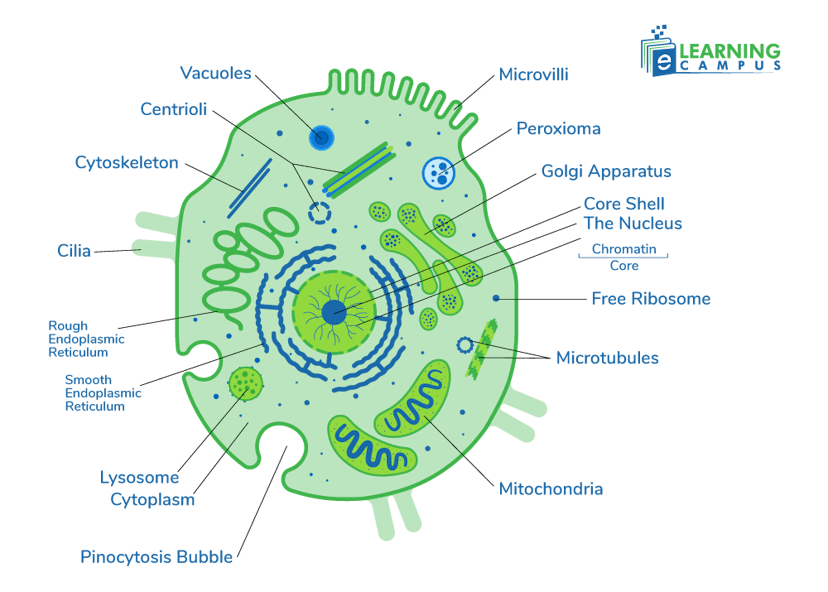
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotes are organisms that are made up of eukaryotic cells. The eukaryotes are divided into two major groups;
- Multicellular
- Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are composed of only one cell that carries out all cellular functions necessary for an organism. It includes fungi and Protista.
Multicellular organisms are made up of many cells and are specialized for different functions. It includes plants and animals.
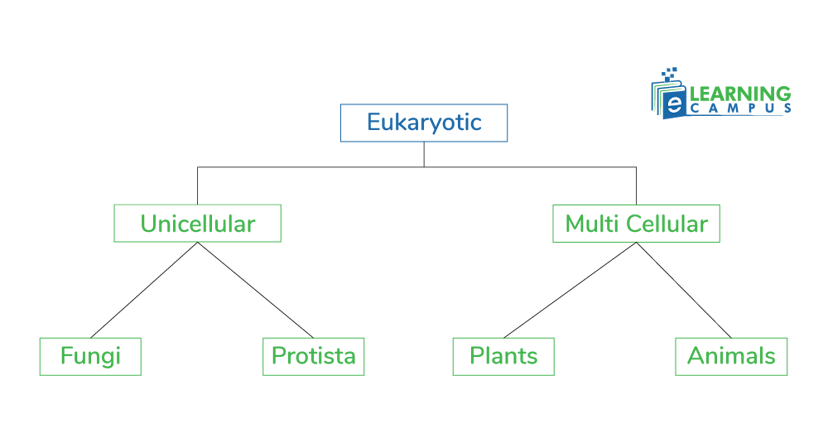
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells Venn Diagram
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells have many differences and similarities. A major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not have a well-defined nucleus. The eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Venn diagram shows the differences and similarities between the two types of cells with the help of overlapping circles.
The below Venn diagram of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells will help you understand the key differences and similarities of the cell.
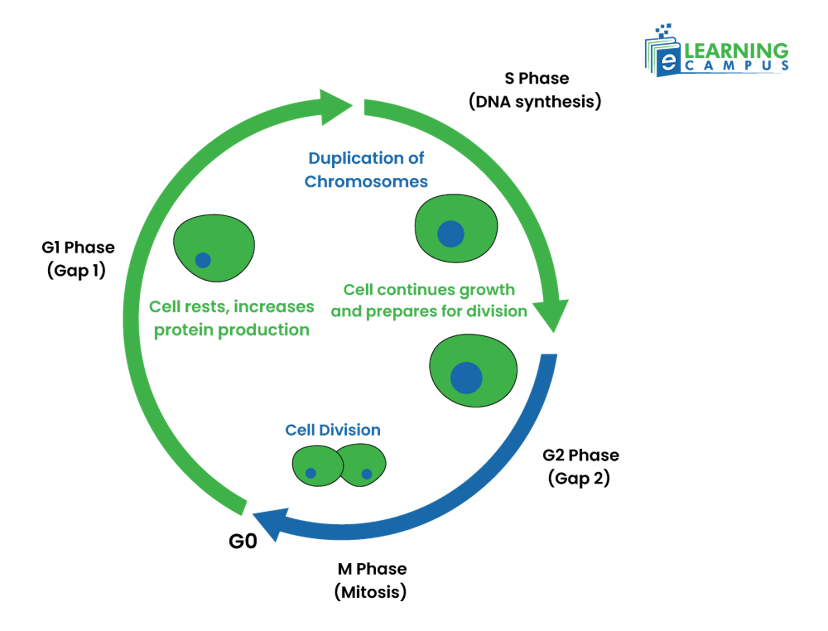
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer
The eukaryotic cell cycle and cancer are closely linked. During eukaryotic cell division, genetic information is passed down to daughter cells in a highly regulated manner. However, sometimes during this process, mistakes occur that lead to uncontrollable cell proliferation, known as cancer.
Let’s look at how the cell cycle happens in eukaryotic cells and how it causes cancer.
In eukaryotic cells, the cycle occurs in five major stages;
- G0: In this stage, the cell performs its normal work in the body.
- G1 (or gap1): In this stage, the cell starts to grow.
- S (or synthesis): In this stage, the cell copies its DNA.
- G2 (or gap2): the cell prepares to divide in the G2 stage.
- M (or mitosis): In mitosis, the cell’s nucleus and cytoplasm divide into two daughter cells.
These stages are important in the cell cycle and the transmission of genetic material. Replication of DNA is crucial in the ‘S’ stage. Several checkpoints in the cycle ensure cell growth, division, and DNA replication. Any mutation of mistakes are reversed and repaired in these stages and prevent them from moving to the next stage.
These checkpoints are controlled by proteins. P53 is a crucial protein that regulates the cell cycle at the G1 phase. If DNA is damaged at this stage, p53 is activated, halting the cycle and facilitating DNA repair.
If this protein, p53, is missing or less active, the cell may enter the next phase with damaged DNA. Due to this, DNA misspellings will transmit to the daughter cells. This error over many cells causes cancer.
Conclusion
Eukaryotic cells are highly complex and organized cells that are the foundation of highly complex organisms such as animals and plants. There are many similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The uncontrollable division of eukaryotic cells is known as cancer.
Learn Science With Us
Are you looking for an expert tutor to learn science from your home? We are at your service. We have professional online science tutors to make science fun for you.
