Distance vs Displacement
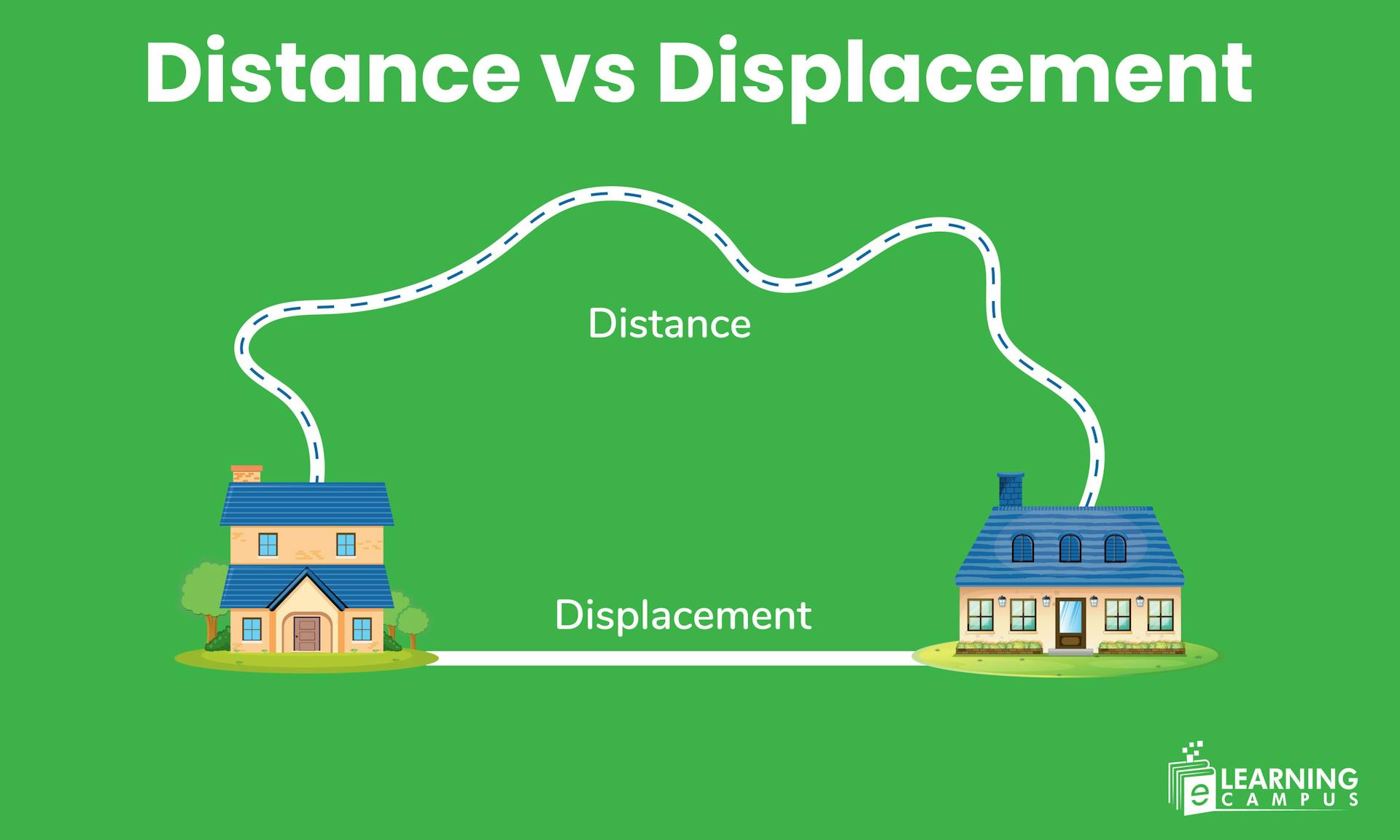
Have you ever been confused between distance and displacement while studying motion in physics? These two fundamental concepts often cause confusion among students. While they might seem similar at first glance, there are crucial differences between these terms.
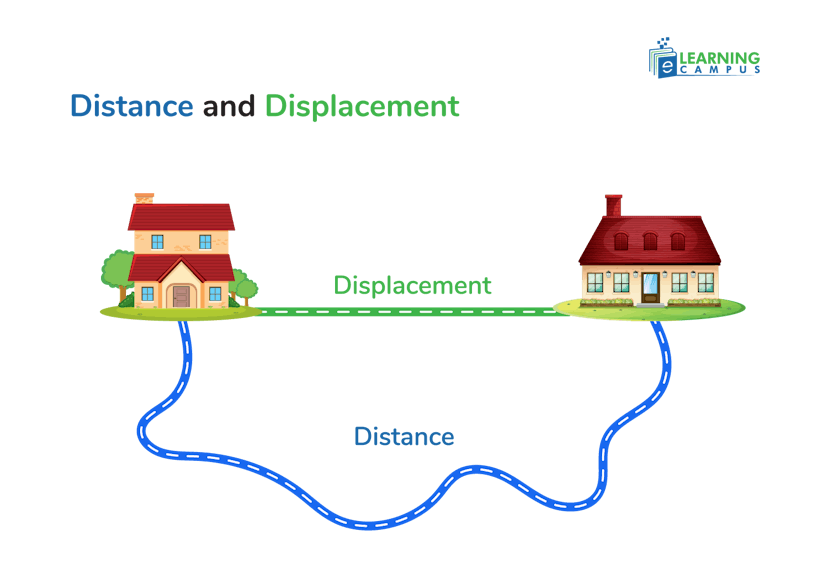
Distance is the total path length covered by an object, while displacement is the straight line distance between an object's starting and ending points, including direction.
In this blog, you will learn about the distance, displacement, and the difference between displacement and distance.
What is Distance?
Distance is the total length of the path traveled between two points, measured in units like meters or miles. It is a scalar quantity that represents the total path length traveled by an object, regardless of direction.
Think of it as the reading on your car's odometer. It simply adds up every meter, kilometer, or mile you travel, without caring whether you are going north, south, or in circles.
Example
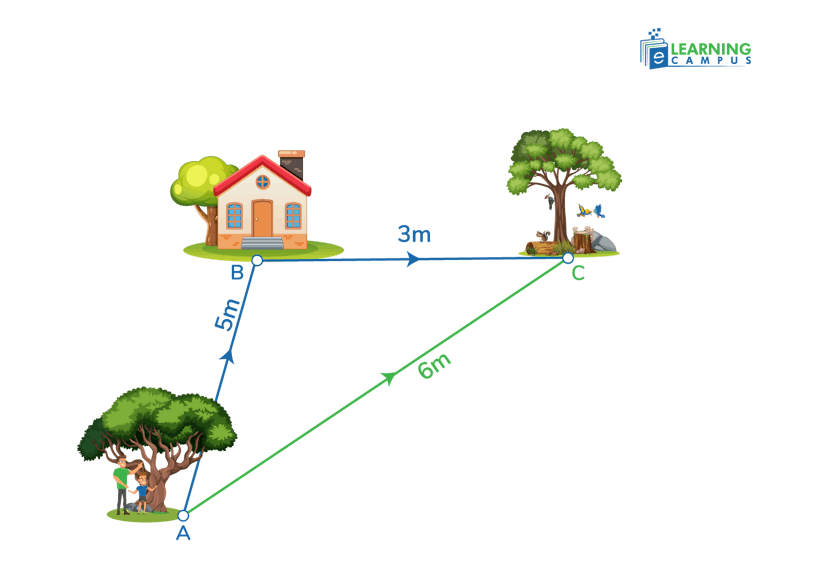
If you drove your car 5 meters from point A to B, then 3 meters from B to C, the total distance traveled is 8 meters. There is no reference to direction. Only the distance traveled is calculated.
How to Calculate the Distance
To calculate the distance traveled by any object, we multiply the object's speed by the time it was moving. The formula to calculate the distance of an object is given as;
distance = speed × time
Example: A car travels at an average speed of 80 km/h for 2.5 hours. Calculate its distance.
We will use the distance formula here.
distance = speed × time
Speed = 80km/h
Time =2.5 hours
Distance =80 km/h×2.5 h=200 km
What is Displacement?
Displacement is the shortest straight-line distance between the starting position and the final position of an object. It is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction.
Unlike distance traveled, which is a scalar quantity and accounts for the total path, displacement can be zero if an object returns to its starting position.
Displacement Formula
The basic formula to find the displacement is given as;
displacement = final position – initial position
Δx=𝑥f−𝑥i
Where,
𝑥f is the final point
𝑥i is the initial point
How to Calculate Displacement
To calculate displacement, we determine the shortest distance and direction from an object's initial position to its final position. To find it, we subtract the initial position from the final position, using the formula.
For one-dimensional motion, the sign indicates direction, such as positive for right, negative for left.
Example 1: A car starts at position 10 meters and ends at position 45 meters along a straight road.
Use the formula
Δx=𝑥f−𝑥i
Δx = 45 m - 10 m = 35 meters
The displacement is 35 meters in the positive direction.
Example 2: Backward Motion
A person walks from position 20 meters to position 5 meters.
Δx=𝑥f−𝑥i
Δx = 5 m - 20 m = -15 meters
The displacement is 15 meters in the negative direction (backward).
Example 3: Returning to Start
A runner completes a lap and returns to the starting line.
Δx=𝑥f−𝑥i
Δx = 0 m - 0 m = 0 meters
The displacement is zero, regardless of the distance traveled.
When Are Distance and Displacement Equal?
Distance and displacement have the same magnitude only when an object moves in a straight line in a single direction without reversing. In all other cases, distance is greater than or equal to displacement.
For instance, if you walk 10 meters due north in a straight line without stopping or changing direction, both your distance and displacement magnitude are 10 meters (with displacement being 10 meters north).
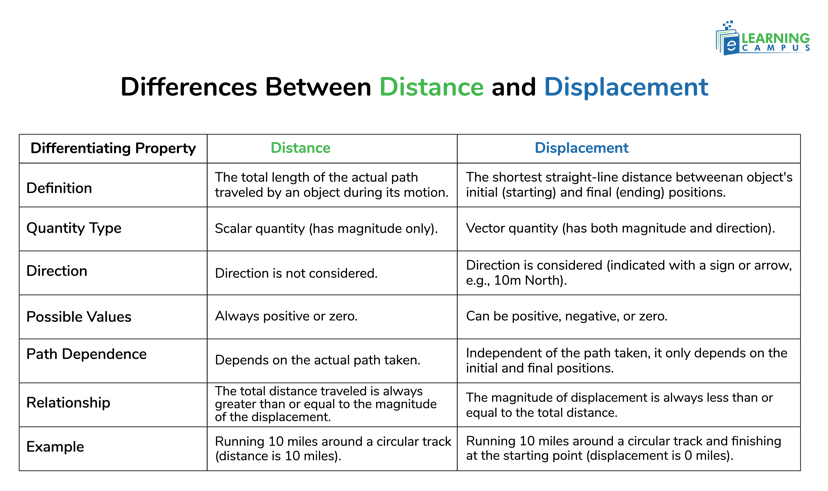
What are the Differences Between Distance and Displacement
Distance and displacement are distinct concepts in physics that describe an object's motion, differing primarily in their consideration of the path taken and direction.
Here are the main differences between distance and displacement.
Distance vs Displacement Worksheet
A distance vs displacement worksheet provides exercise that helps students practice the concepts of distance and displacement by comparing them. These worksheets present problems that require calculating the total path length (distance) versus the straight-line change in position from start to finish (displacement) using everyday examples like a baseball diamond or a running track.
Below, you can download a printable practice distance vs displacement worksheet with answers in PDF
Download WorkSheet
Conclusion
Distance is the total path length traveled by an object, while displacement is the straight-line distance between an object's initial and final positions, with direction considered. Distance is a scalar quantity that has magnitude only. In contrast, displacement is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Learn Physics Online
Are you struggling with Physics concepts and don’t know how to prepare for exams? We can help you. We have expert online Science tutors with years of experience in teaching physics online. They teach according to your needs. You will get individual guidance and targeted preparation for your exams.
