Cardiac vs Skeletal Muscle
Muscles play a vital role in movement, stability, and other bodily functions. Cardiac and skeletal muscles are different muscles that perform different functions. Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and are responsible for the continuous pumping of blood throughout the body, and skeletal muscles are attached to the bones and maintain movement and posture.
In this blog, you will learn about cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle, the structure of cardiac and skeletal muscle, their functions, and differences.
What are Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscles are a specialized type of muscle tissue that are found only in the heart. It is also known as myocardium. Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles. It means their function can not be controlled by human actions.
Structure of Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle has a complex structure. It has a striated appearance and branched cells with an involuntary control mechanism.
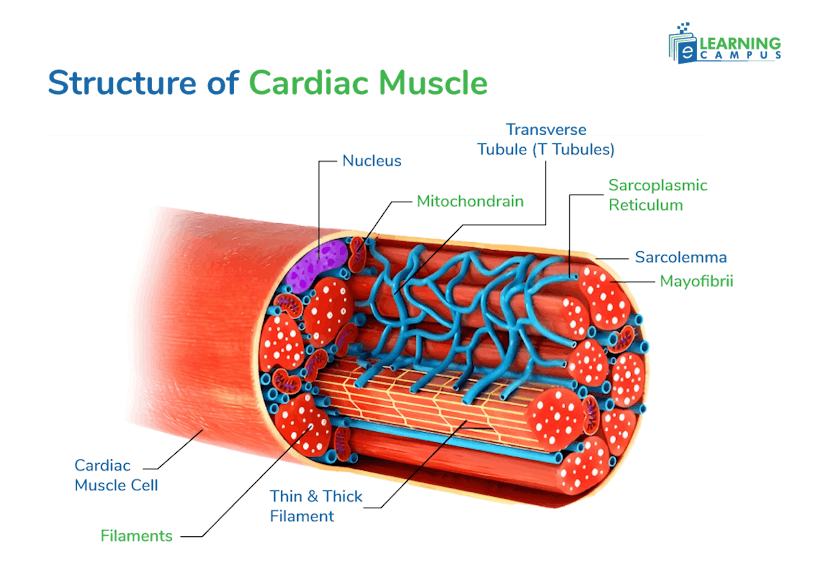
Cardiomyocytes
Cardiac muscle cells are made up of individual cells called cardiomyocytes.
Striated Appearance
Cardiac muscles have a striated appearance. It is due to the organized arrangement of contractile proteins, such as actin and myosin that are found within sarcomeres.
Branched Cells
Cardiac muscles have branched cells due to the interconnectedness of cells. The cells are interconnected by the intercalated disc.
Mitochondria
There are several mitochondria in cardiac muscle. They act as the powerhouse of energy. As the cardiac muscles function nonstop, they need more energy. Therefore, cardiac muscles are rich in mitochondria.
T Tubules
T tubules, known as transverse tubules, help in muscle contraction by acting as conduits for electrical signals. They ensure rapid and coordinated muscle activation.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
The Sarcoplasmic Reticulum regulates calcium ion concentration within the muscle cell. It acts as a storage and release site for calcium ions.
Nucleus
Each cardiac muscle contains one nucleus. It is situated in the middle of the cardiac muscle cell.
Functions of Cardiac Muscle
The cardiac muscles play an important role in the function of the heart, including the circulation of blood throughout the body.
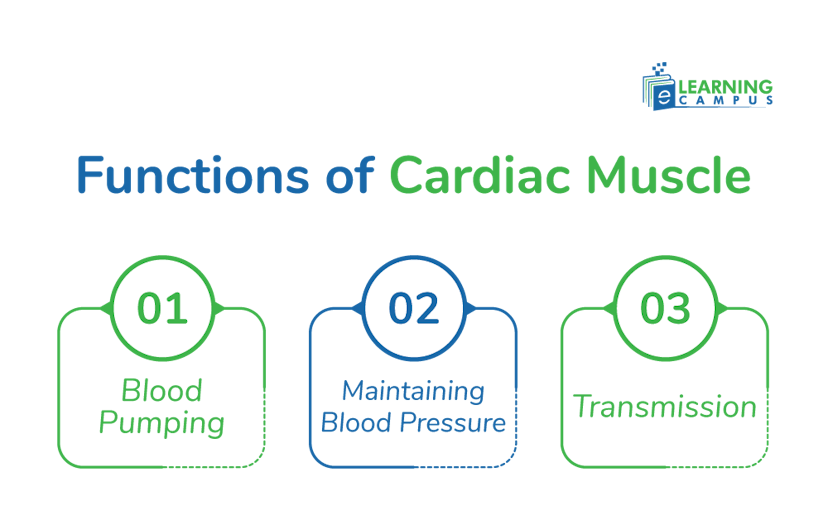
Blood Pumping
The primary function of cardiac muscle is to help pump blood through the body. These muscles contract and relax rhythmically to propel blood from the chambers of the heart into the circulatory system. The blood circulation is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body cells.
Maintaining Blood Pressure
The rhythmic contractions of cardiac muscle help maintain blood pressure. It maintains proper circulation throughout the body.
Transmission
The cardiac muscle contains a specialized structure called the intercalated discs. It transmits electric signals from one cell to another to maintain synchronization in contraction.
What are Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are the muscles that are found attached to the bones. It plays a vital role in locomotion, breathing, and stabilizing joints. It comprises 30% to 40% of total body mass. These are voluntary muscles. It means they can be controlled consciously by the somatic nervous system.
Structure of Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle tissue is composed of elongated, multinucleated muscle fibers that are bundled together and surrounded by connective tissue sheaths
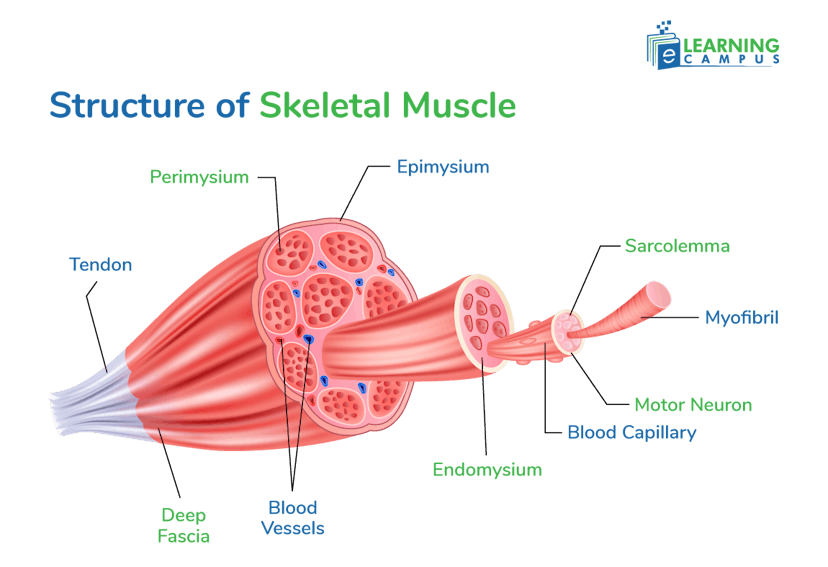
Muscle Fibers
Skeletal muscle is composed of individual cells known as muscle fibres. It contains multiple nuclei and specialized structures like myofibrils.
Myofibrils
Myofibrils are the cylindrical organelles found within muscle fibers. These are composed of protein filaments, such as actin and myosin. They help in muscle contraction.
Sarcomeres
Sarcomeres are the functional units of myofibrils. Their repeated structure gives a muscle striated appearance.
Tendons
Tendons attach muscle to the bone throughout the body. These are made up of connective tissues.
Connective Tissue Sheaths
The connective tissue provides structural support, transmits forces generated during muscle contraction, and helps to organize and compartmentalize muscle fibers. It has three layers.
- Epimysium: It encloses the entire muscle and provides structural support.
- Perimysium: It surrounds bundles of muscle fibers, such as fasciculi, and provides structure and organization to muscle.
- Endomysium: It encloses individual muscle fibers and facilitates nerve and blood supply.
Functions of Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles play an important role in body movement and structure. They carry out various functions, such as movement, posture, joint stability, and heat generation. We will discuss the functions below in detail.
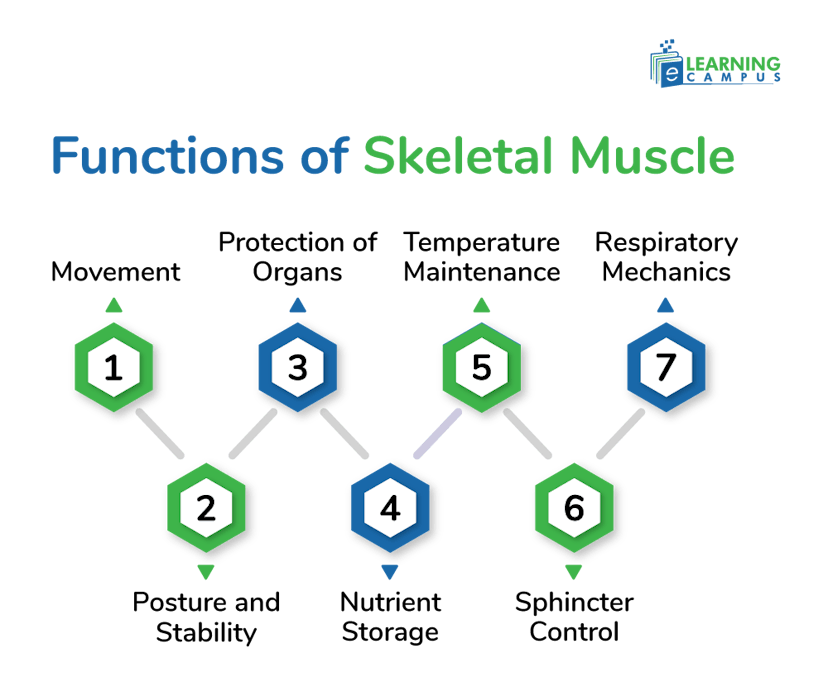
Movement
The primary function of skeletal muscles is to support body movement, such as walking, running, and lifting. The contraction of muscle pulls tendons on bones that cause movement of the bones.
Posture and Stability
Skeletal muscles maintain body posture and stability. They hold the body upright and prevent falls. The gluteal muscle helps stabilize joints, preventing dislocations and misalignments.
Protection of Organs
Skeletal muscles act as a protective barrier for internal organs. They protect organs from injury, especially those in the abdomen and pelvis.
Nutrient Storage
Skeletal muscles also act as the storage site for nutrients that are important for muscular actions. They store glycogen and amino acids, which can be used as fuel or building blocks for protein synthesis when needed.
Temperature Maintenance
When the body temperature drops, the brain signals skeletal muscles to contract. It causes shivering and produces heat as a byproduct. This heat production helps to raise and maintain body temperature within the normal range. Muscle contraction requires energy (ATP), and the breakdown of ATP releases heat, which contributes to maintaining body temperature.
Sphincter Control
Skeletal muscles form sphincters that control the openings of the digestive and urinary tracts. It helps in swallowing, urination, and defecation.
Respiratory Mechanics
These muscles have a vital role in respiratory mechanisms. The diaphragm and other muscles involved in breathing are skeletal muscles. They help in inhaling and exhaling oxygen.
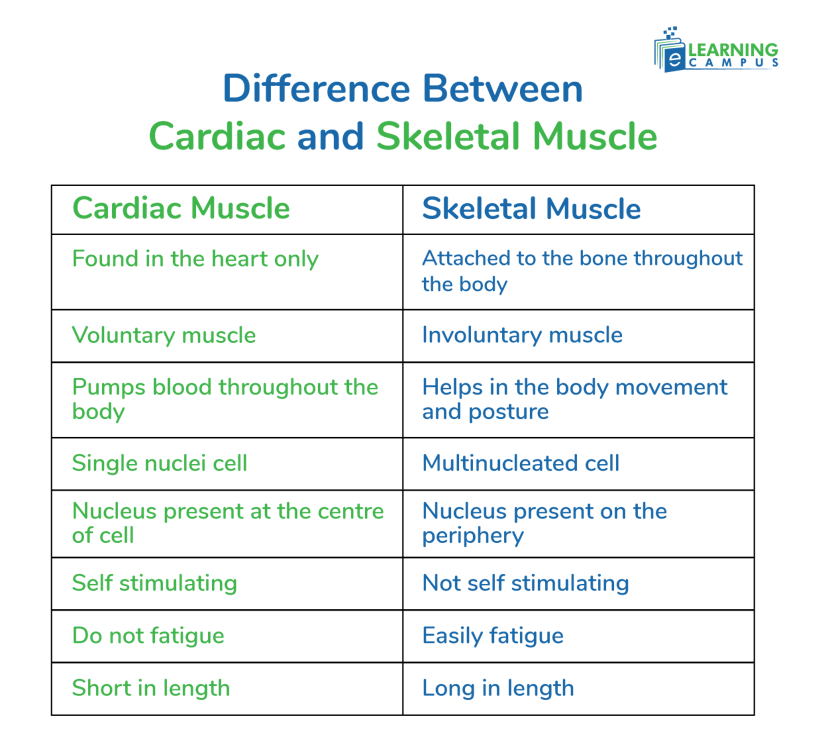
Difference Between Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal and cardiac muscles are two important types of muscle that play an important role in the body. The difference between the skeletal and cardiac muscle lies in their location, structure, and functions.
Conclusion
The cardiac and skeletal muscles are different muscles found within the body. They have a vital role in the proper functioning of the body. The cardiac muscle is located in the heart and helps in pumping blood in the body. The skeletal muscles are found attached to the bones and are responsible for bodily movement.
