Apoptosis- A Programmed Cell Death
Apoptosis is a process of programmed cell death that plays a crucial role in the development and health of multicellular organisms. It is a highly regulated mechanism that eliminates unwanted or damaged cells. The cellular apoptosis helps to maintain tissue homeostasis and prevent diseases. In this blog, you will learn about apoptosis, the pathways of apoptosis, its steps (morphology), and its importance.
What is Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a Greek word which means ‘dropping or falling off.’ In biological terms, apoptosis is a process of programmed death of cells through which our body gets rid of damaged and unwanted cells. For example, a cell with damaged DNA can replicate itself, leading to cancer. Apoptosis can prevent it from happening.
Apoptosis Pathways
Apoptosis pathways are the cellular mechanisms through which apoptosis is initiated. There are two apoptotic pathways, namely the intrinsic pathway and the extrinsic pathway. We will discuss these pathways in detail.
Intrinsic Pathway
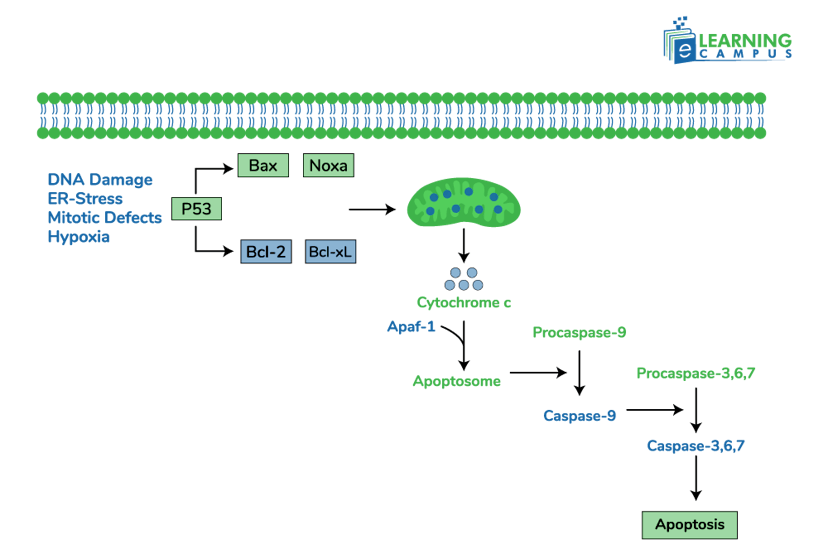
The intrinsic pathway of apoptosis, also known as the mitochondrial pathway, is initiated by internal cellular events that signal the need for cell death. These events include DNA damage, biochemical stress, and the absence of growth factors.
- Biochemical stress: Apoptosis is initiated due to disruptions in cellular metabolism. Such as the accumulation of misfolded proteins or oxidative stress.
- DNA Damage: If DNA is damaged, the cell can initiate apoptosis to prevent the propagation of harmful mutations.
- Lack of growth factors: The absence of growth factors that promote cell survival can also initiate apoptosis.
Key Steps and Mechanisms
- Various stimuli, such as DNA damage and growth factors, can initiate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway.
- Bcl-2 family proteins regulate mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Pro-apoptotic enzymes like Bax and Bak insert into the mitochondrial membrane and form pores.
- When MOMP occurs, cytochrome c is released from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm.
- Cytochrome c binds to Apaf-1 and procaspase-9. It forms a complex called the apoptosome.
- The apoptosome activates caspase-9. This activates downstream effector caspases like caspase-3 and caspase-7, leading to the execution of apoptosis.
- The activated caspases split cellular proteins, causing cell shrinkage, DNA fragmentation, and ultimately, cell death.
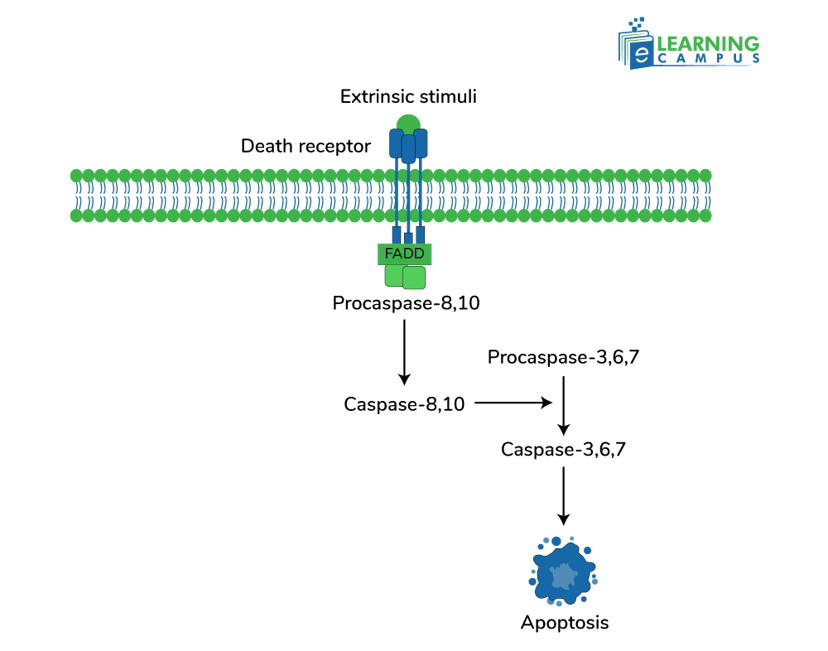
Extrinsic Pathway
The extrinsic pathway, also known as the death receptor pathway of apoptosis, is a cellular mechanism that causes programmed cell death through external signals. It involves the binding of death ligands (an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom or ion to form a coordination complex) to death receptors on the cell surface. It initiates a chain of events that ultimately leads to the dismantling of the cell.
Key Steps and Mechanisms
- The extrinsic pathway begins with the binding of specific death ligands, such as Fas ligand, TNF-alpha, to their corresponding death receptors, Fas, TNFR1, on the cell membrane.
- This binding recruits adaptor proteins like FADD (Fas-associated death domain) and TRADD (TNFR1-associated death domain), which contain death domains (DDs).
- The adaptor proteins then bind and activate initiator caspases, like caspase-8 and caspase-10, forming a DISC.
- The close proximity of procaspases within the DISC allows for their auto-catalytic activation, splitting themselves and becoming active caspases.
- Activated caspase-8 and caspase-10 can then split and activate downstream executioner caspases, like caspase-3, -6, and -7.
- The activated executioner caspases initiate a chain of proteolytic events that dismantle the cell.
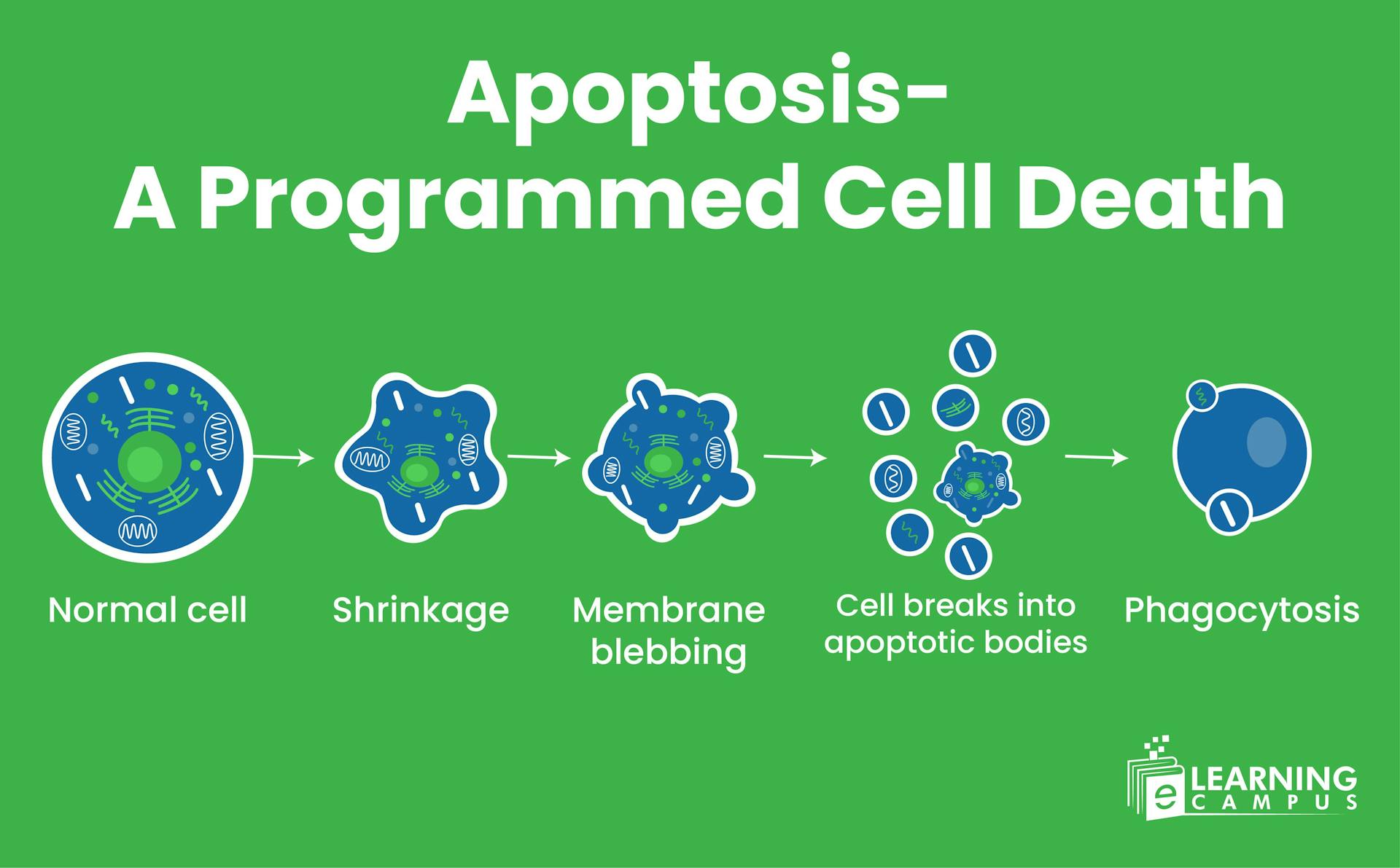
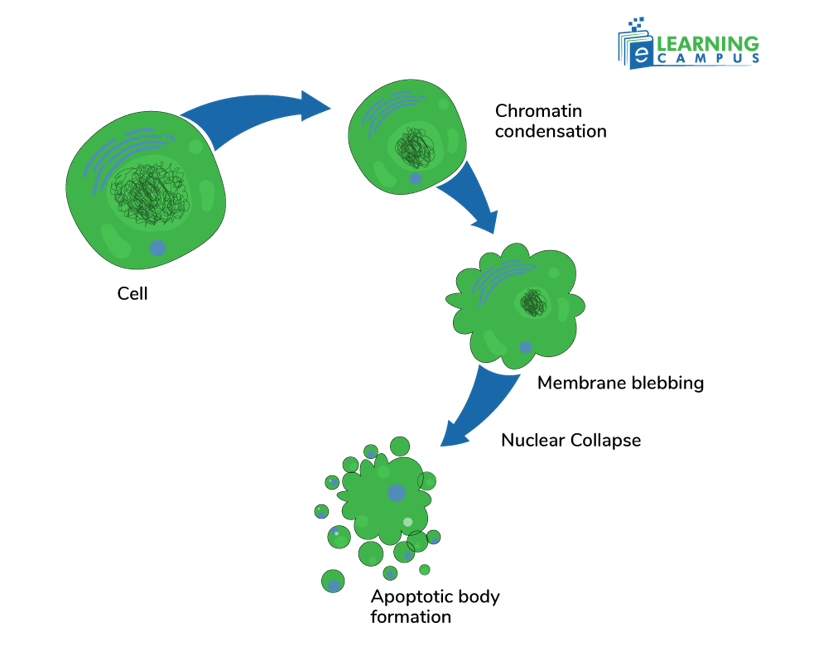
Morphology of Apoptosis
Apoptotic cells were first distinguished from healthy cells by certain morphological features. These cells are characterized by cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, and formation of apoptotic bodies.
Cell Shrinkage
Cell shrinkage is the initial morphological evidence of cell death. As the cell shrinks, the K+ and Na+ ions are lost, which are the primary ingredients of the cell volume along with water. In this phase, the cell decreases in size, and the cytoplasm becomes more dense.
Chromatin Condensation
The DNA within the nucleus condenses and aggregates, often forming a crescent shape around the nuclear membrane. This is also known as pyknosis.
Membrane Blebbing
Due to the separation of the plasma membrane from the cytoplasm cell membrane develops irregular protrusions called blebs. It continues until the cell forms apoptotic bodies in the condensation stage.
Importance of Apoptosis
Apoptosis is also referred to as ‘cell suicide’. It has high importance for healthy body formation and maintenance. It maintains tissue homeostasis, proper embryonic development, and immune system function. The importance of this process is discussed below.
Embryonic Development
Apoptosis plays a significant role in shaping the body during embryonic development. It eliminates cells that are no longer needed. For example, the webbing between fingers and toes.
Tissue Homeostasis
It removes old, damaged, or excess cells to maintain the proper size and number of cells in tissues. The homeostasis ensures that tissues function properly.
Elimination of Damaged Cells
Apoptosis helps remove cells with damaged DNA or those infected with viruses or bacteria. It prevents the spread of infections and potential harm.
Eliminating Cancerous Cells
The process of apoptosis eliminates the cells with the cancerous mutation. It prevents tumor formation in the cells.
Conclusion
Apoptosis is a biological process in multicellular organisms that eliminates dead and unnecessary cells without causing damage to surrounding tissues. This process is essential for development, tissue homeostasis, and prevention of disease.
Learn Biology With eLearning Campus
Are you looking to hire an online tutor for Biology? We can help you. We have expert tutors for science subjects to make lessons interactive and engaging. We will help you in targeted preparation for your exams.
